The brown recluse is one of the most dangerous spiders in North America, it is also one of the most misidentified. Knowing what the brown recluse looks like, whats its preferred habitat and its behavior can help you quickly identify the brown recluse.
There are also a number of spiders that are confused with the brown recluse, which are listed below to help you tell the two apart.
Table of Contents
What Are Brown Recluse Spiders
The brown recluse spider is also referred to as the violin spider. This spider has six eyes and has a distinct violin marking on its head space that points towards the back.
The violin marking can often be misidentified with other spiders, such as the cellar spider.

Habitat and Distribution
The brown recluse has a documented range in the United States that runs south of southeastern Nebraska, through southern Iowa and Illinois, along with Indiana then to southwestern Ohio.
In the southern areas, it can be encountered from Texas to Georgia, along with north to Kentucky. The spider has not established itself outside this native range, even though there are rumors that it has been seen in California.
Behavior
The brown recluse may lower its body and pull its two front legs backward in a defensive pose when alarmed.
The back legs may be pulled backward, enabling the spider to lunge forward, while keeping the pedipalps raised.
The good news is that this spider will normally try and get away, avoiding conflict where possible. If detained, it is known to assume a lifeless pose, where it plays dead.
How to Identify a Brown Recluse
There are some things to look for, helping you quickly identify if the spider you have encountered is a brown recluse.
Location
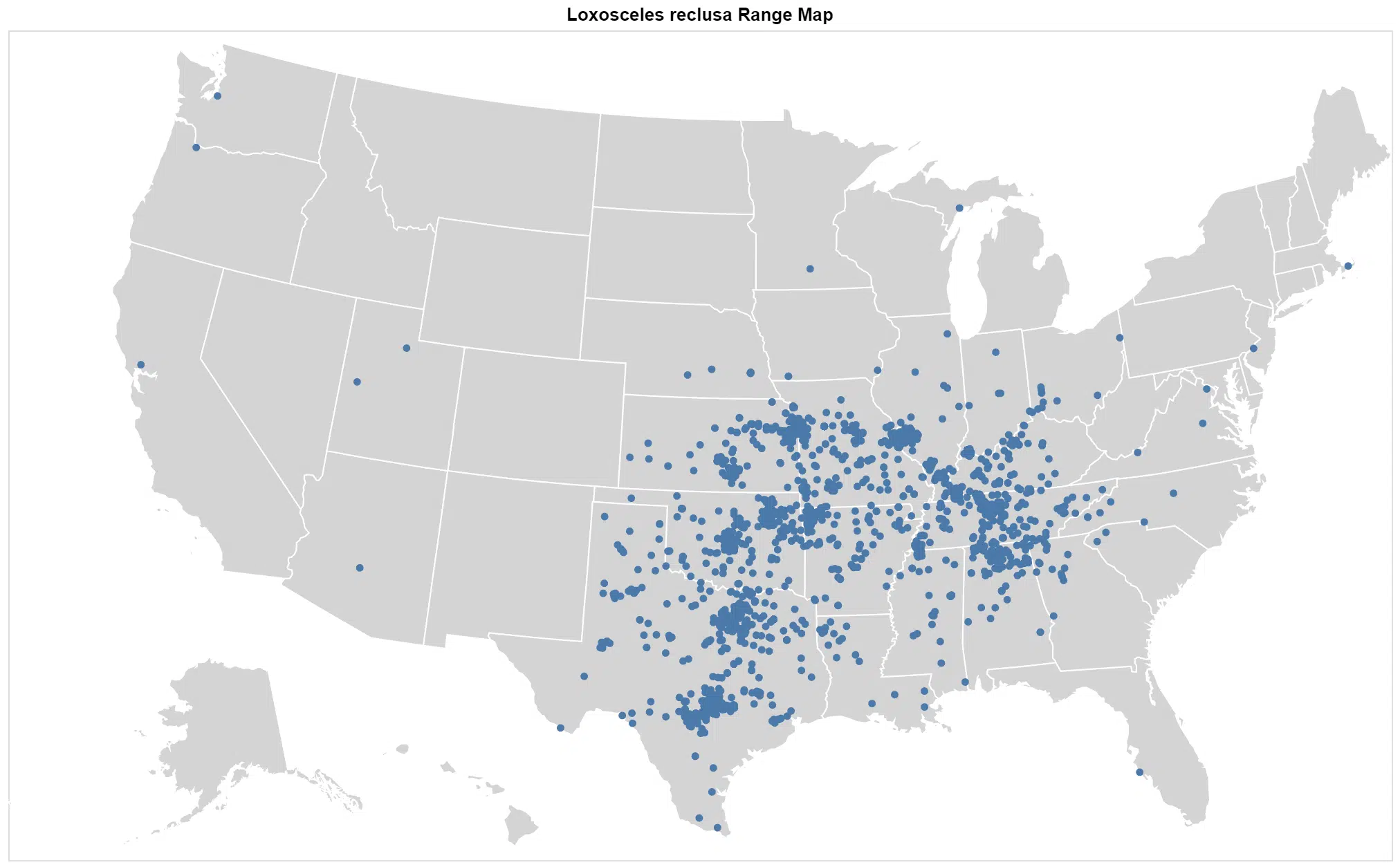
The brown recluse is a common and widespread brown spider that is found only in the central and southern parts of the United States.
They can be found in Alabama, Arkansas, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, Ohio, Oklahoma, Tennessee, and Texas.
If you are not in one of these areas then chances are it is not a brown recluse you have encountered.
Size

An adult brown recluse can grow to 8mm in body length, 16mm in width, and have a leg span of 24mm.
Males have longer legs than the female, but their body size is smaller.
3 Pairs of Eyes

Most spiders have eight eyes, but the brown recluse only has six, which helps with identification. The eyes are arranged in pairs, set in a semicircle on the front of the head space. They have one median pair and two lateral pairs.
Cephalothorax
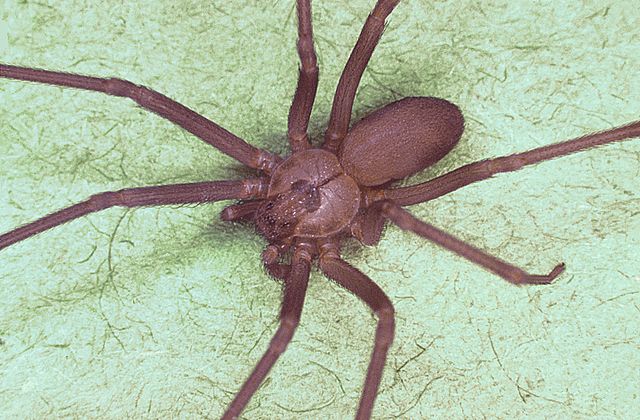

The cephalothorax, or head space, is the portion of the spider where the legs attach.
In the brown recluse, this is where the spider has a brown violin shape with the neck of the violin pointing towards the back of the spider.
Abdomen
The abdomen attaches to the cephalothorax and can vary in color from dark brown to cream. The spider will never have two colors, they will always be one uniform color.
Legs

Their legs are uniform in color with no banding or stripes. There are no spines on the legs, though there are fine hairs.
Activity
The brown recluse is active at night and spends the day hidden. They build their webs on wooden surfaces, such as furniture, boxes, walls, and frames. They are often encountered in basements and attics.
Web
The brown recluse spins silk, which is unlike other spiders. A spider’s silk is usually round, but the silk fibers from a brown recluse are flat and thin.
When it comes to the web of a brown recluse, there are two questions you want to ask yourself to help you identify if it is a brown recluse web.
Are there any insects caught in the web?
The brown recluse is a hunting spider and chases its prey rather than using its web to entrap prey.
If you see large webs between the branches in your yard or around the home filled with insets, then it is probably not a brown recluse.
The brown recluse will spin its web retreat out of sight.
Is the web in a crevice?

The brown recluse is likely to build its web in an undisturbed location. Remember they only create webs as a retreat and to lay eggs.
Their webs are often found in dark and dry areas, such as inside furniture, in basements, or storage boxes.
They are also known for building webs in old clothing and shoes you haven’t worn for a while, which is what increases the risk of being bitten.
Spiders That Look Like Brown Recluse
There are 29 spiders in the United States that are often confused with the brown recluse, these include:
1. Southern House Spider

Scientific name: Kukulcania hibernalis (formerly Filistata hibernalis).
Common name: Southern house spider.
A female southern house spider can grow to 0.74 inches (19mm) in body length with males being slightly smaller at 0.39 inches (10mm) in body length.
The males are brown or amber, while the females can be charcoal, black or brown. Both have light gray velvet type hair on their abdomen.
It’s not uncommon to confuse the male southern house spider with a brown recluse.
Brown Recluse vs Southern House Spider
- Larger in size
- Light gray velvet hair on the abdomen
- There is no dark brown violin marking on the cephalothorax
2. Arizona Black Hole Spider
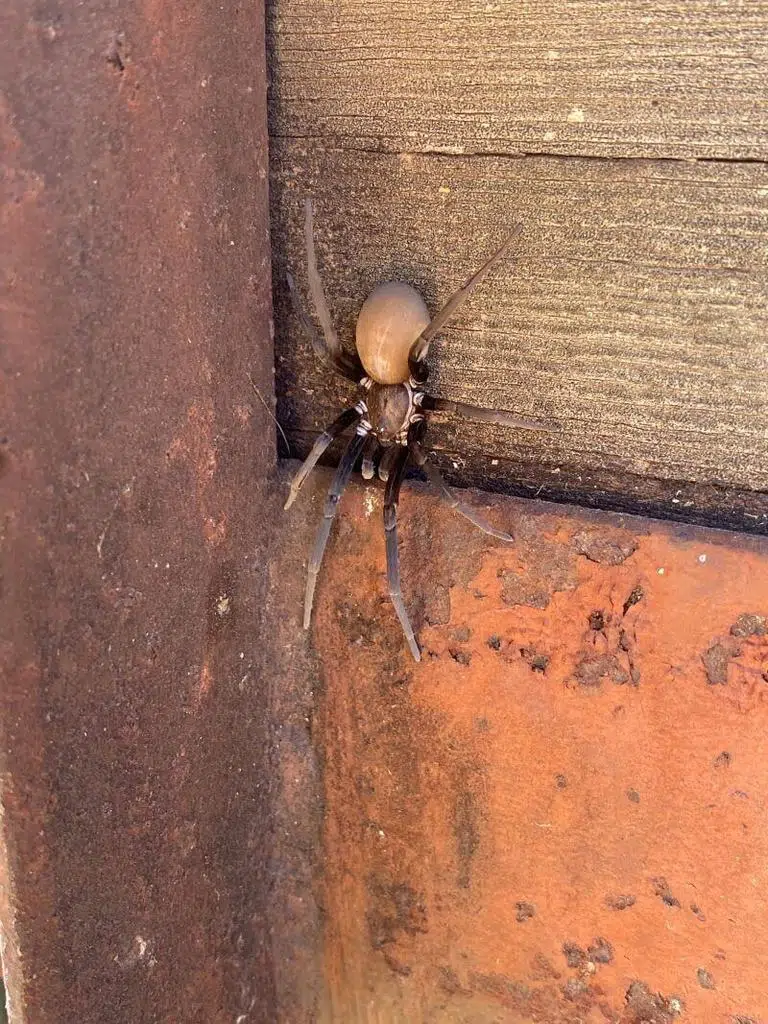

Scientific name: Kukulcania arizonica.
Common name: Arizona black hole spider.
The Arizona black hole spider can be found in Arizona, Nevada, New Mexico, and California and is a black spider with a velvet texture.
Females grow to 13mm in body length, while males are thinner with longer legs.
These spiders build their webs in the crevice of buildings and the males are often confused with the brown recluse.
Brown Recluse vs Kukulcania Arizonica
- Usually black in color not brown
- No violin marking on the cephalothorax
3. Giant House Spider
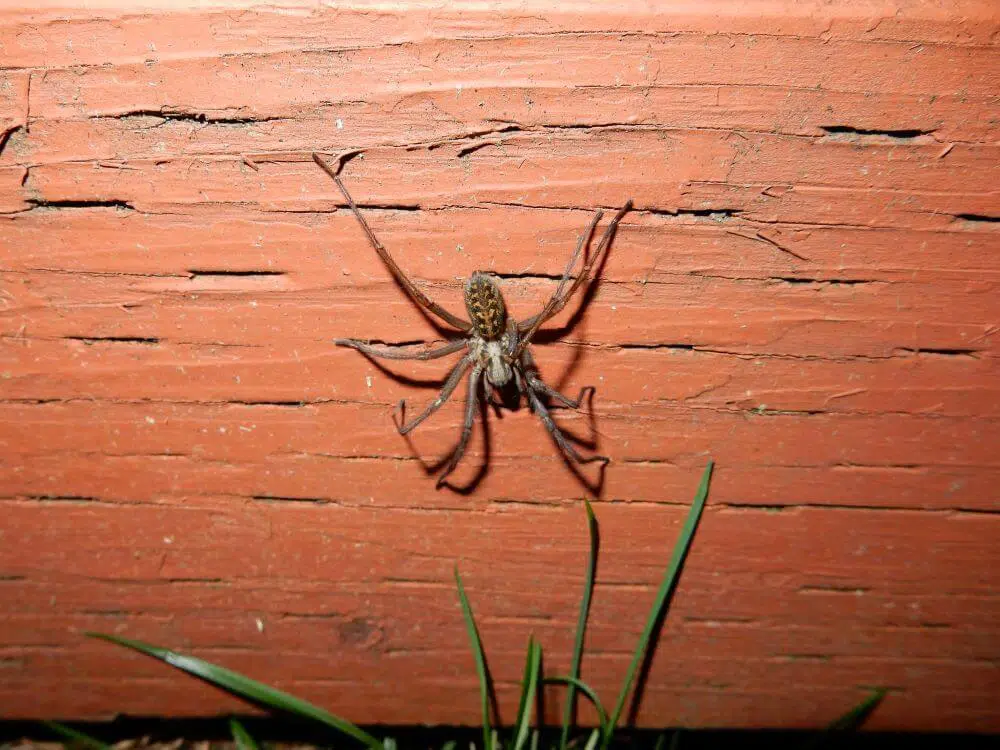

Scientific name: Eratigena duellica.
Common name: giant house spider.
The giant house spider is a dark brown spider with lighter markings on the sternum. There are three light spots on each side, that form an arrow shape that points towards the spider’s head. They can be brown, yellow, or red in color with hairy legs, abdomen, and pedipalps.
Females are larger than the male, growing to 0.73 inches (18.5mm) in body length, males are smaller growing to 0.59 inches (15mm) in body length.
Their eight eyes are equal in size, arranged in two rows.
Brown recluse vs Giant House Spider
- Three light dots on each side, forming an arrow pointing towards the head
- No violin shape pointing towards the abdomen
- Hairy legs
- Larger than the brown recluse
4. Barn Funnel Weaver

Scientific name: Tegenaria domestica.
Common name: barn funnel weaver (in North America), domestic house spider (in Europe).
Barn funnel weavers have a flattened cephalothorax, straight abdomen, and an elongated body.
Females can grow to 11.5mm in body length, with males being slightly smaller at 9mm.
The males have longer legs.
These spiders range from being and dark orange to brown with striped legs and two black stripes on the cephalothorax. The abdomen has a chevron pattern.
Brown Recluse vs Barn Funnel Weaver
- Striped legs
- Black stripes on cephalothorax
- Chevron pattern on the abdomen
- No violin marking on the cephalothorax
5. Hobo Spider

Scientific name: Eratigena agrestis.
Common name: hobo spider.
The hobo spider can grow to 14mm in body length with brown coloration.
They have no banding on the legs.
The abdomen has a chevron pattern, with the chevrons pointing towards the head. They also have a light stripe that runs down the sternum and a diffused pattern on the cephalothorax.
Brown Recluse vs Hobo Spider
- Chevron pattern on the abdomen
- Light stripe run down the sternum
- Diffused pattern on the cephalothorax
- No violin marking
6. Desert Grass Spider
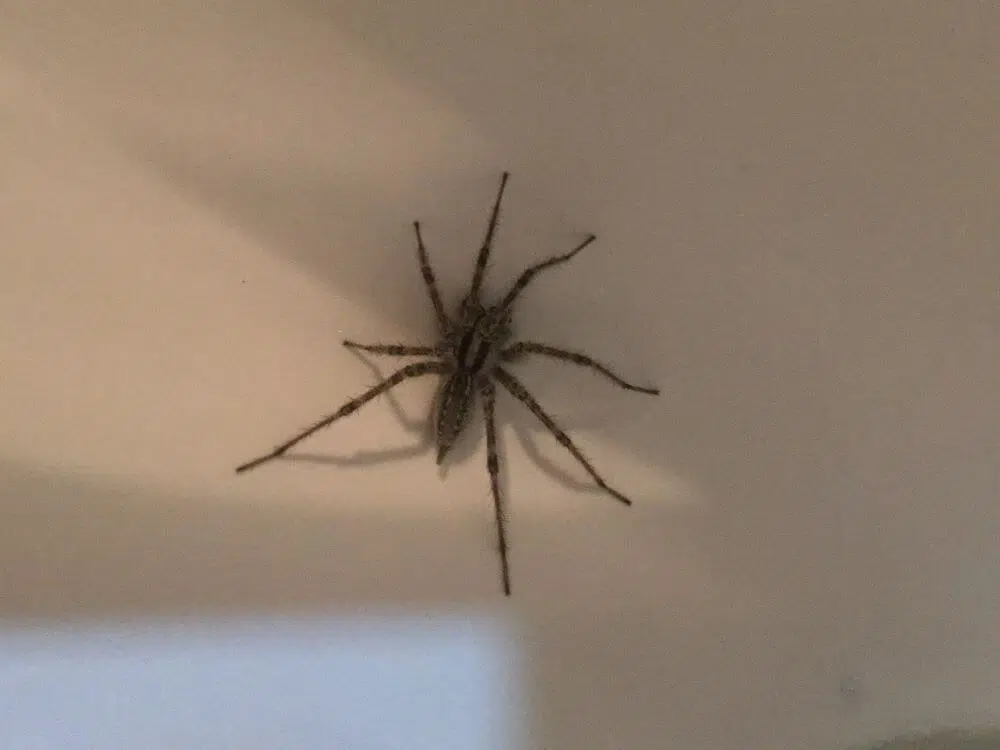

Scientific name: Agelenopsis aperta.
Common name: desert grass spider, funnel-web spider.
The desert grass spider can be black, brown, or gray. The cephalothorax can be tan or gray with two brown stripes, the abdomen is tan with two black stripes.
They have long legs, which enable them to run fast.
These spiders can grow to 18mm in body length.
They have eight eyes, arranged in an arc of two rows.
Brown Recluse vs Desert Grass Spider
- Tan or gray cephalothorax with two brown stripes
- Tan abdomen with two black stripes
- Eight eyes arrange in an arc
- No violin on the cephalothorax
7. Long-bodied Cellar Spider

Scientific name: Pholcus phalangioides
Common name: daddy long-legs spider, long-bodied cellar spider, skull spider.
Long-bodied cellar spiders are often referred to as daddy long legs.
Females are slightly larger than males, growing to 8mm in body length.
They have very thin, long legs with thin gray bristles.
Their cephalothorax is peanut-shaped with a translucent body of pale brown with a dark spot on the back. They also have some spots on the back of their abdomens.
They have eight eyes arranged as a single pair in front and three parallel rows of larger eyes.
Brown Recluse vs Long Bodied Cellar Spider
- Long thin legs covered in gray bristles
- Eight eyes
- Translucent body with a dark spot on the back
- Spots on abdomen
8. Marbled Cellar Spider

Scientific name: Holocnemus pluchei.
Common name: marbled cellar spider.
The marbled cellar spider can grow to around 7.5mm in body length with long legs that have black and white circles at the joints.
They have a black stripe down their belly and the abdomen is light brown to gray with a clear white marble pattern.
Brown Recluse vs Marbled Cellar Spider
- Long fragile legs with black and white circles at joints
- Black vertical stripe down the underside
- Light brown to gray with a white marbled pattern
9. Cellar Spider
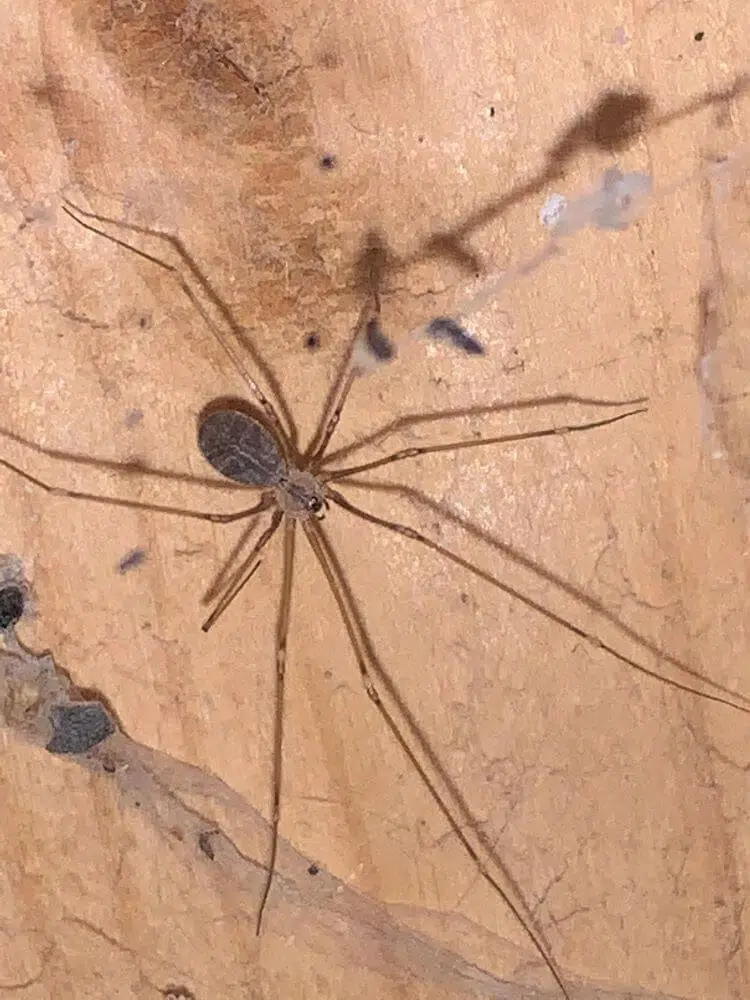

Scientific name: Pholcus manueli.
Common name: cellar spider, daddy longlegs.
The cellar spider prefers dark and hidden places. They are almost transparent, which helps them hide in plain sight.
Their body length is around 8mm with a 25mm leg span.
As the old wives tale has it, these are the most dangerous spider with their venom being the most lethal, but their mouths and fangs are too small to bite a human.
Brown Recluse vs Cellar Spider
- Translucent coloration
- Long spindly legs
- No violin-shaped marking
10. Tailed Cellar Spider
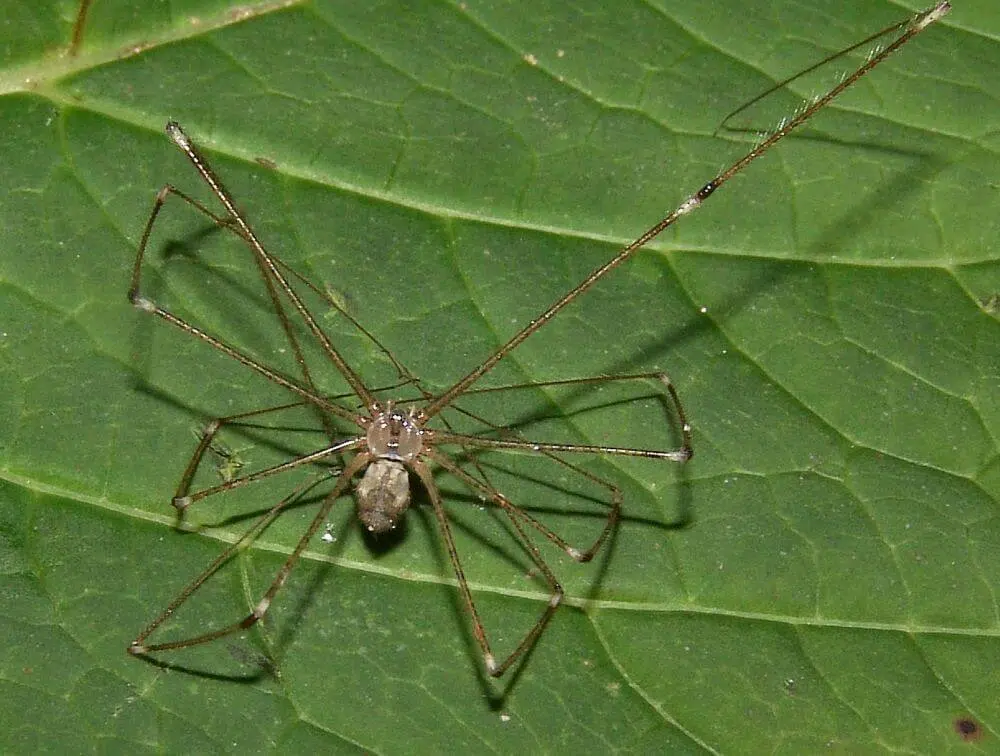

Scientific name: Crossopriza lyoni.
Common name: tailed cellar spider, tailed daddy longlegs spider, box spider.
Tailed cellar spiders can grow to 7mm in body length for females, with males being slightly smaller, growing to 6mm in body length.
They have very long and fragile legs. The legs are gray in color with brown spots. Their knee joints are brown and at the end of the femur and tibia are white.
Their cephalothorax is gray to white, maybe even a pale amber color.
Their six eyes are white in color and located on the tip of the cephalothorax in three rows.
The abdomen is gray with white stripes and dark patches on the sides.
Brown Recluse vs Tailed Cellar Spider
- Gray legs with dark spots
- Gray white to amber colored in the cephalothorax
- Gray abdomen with white stripes and dark patches on the sides.
- Eyes in three rows
11. Woodlouse Spider

Scientific name: Dysdera crocata.
Common name: woodlouse hunter, sowbug hunter, sowbug killer, pillbug hunter, slater spider.
The female woodlouse spider can grow to 15mm with males being smaller and growing to 10mm in body length.
Their cephalothorax is an orange to red color with six eyes, while their legs match the cephalothorax coloration. The abdomen is yellow-brown to beige or brown and shiny.
This spider is seldom found near human habitats.
Brown Recluse vs Woodlouse Spider
- Woodlouse spiders are larger than the brown recluse
- Orange to red cephalothorax and legs
- Pale beige to yellow-brown abdomen that is shiny
12. Oblong Running Spider

Scientific name: Tibellus oblongus.
Common name: Oblong running spider.
Oblong running spiders are long and flattened spiders. They are also hairy. The cephalothorax is red-brown to light brown with a dark brown stripe and a pair of faint stripes. The median stripe is forked. The head is angled in an upward position.
The eight eyes are in two rows of four.
They have a long and cylindrical abdomen that is brown to yellow-brown with dark brown markings. There is a broad dark brown stripe and two faint lateral stripes with a black spot near the end of each lateral stripe.
Brown Recluse vs Oblong Running Spider
- Light brown to red-brown cephalothorax with dark brown stripe and lighter lateral stripes
- Eight eyes in two rows
- Yellow-brown to brown abdomen with dark brown markings with dark brown stripe and two faint lateral stripes
- Small black spot near the end of each lateral stripe
13. Eurasian Running Crab Spider

Scientific name: Philodromus dispar.
Common name: Eurasian running crab spider.
The Eurasian running crab spider is often encountered on bushes and trees, where it is an agile hunter.
Males are shiny black or dark brown with white edging, while females can vary in color and size.
These are small spiders that only grow to around 5mm in body length.
They are ambush predators and do not build a web to ensnare their prey.
Brown Recluse vs Eurasian Running Crab Spider
- Shiny black to dark brown body with white edging
- Small spiders of no more than 5mm in body length
- Not found in homes, but rather on bushes and in trees
- No violin shape on the cephalothorax
14. Red Running Crab Spider

Scientific name: Philodromus rufus.
Common name: Red Running Crab Spider.
The red running crab spider is a small and hairy spider that is distributed throughout the United States. They are very small spiders, often found in shrubs, deciduous trees, and in or on buildings.
Females grow to 3.75mm in body length, with males being slightly smaller at 3.40mm in body length.
The cephalothorax is flattened with smooth lateral margins in a yellow-brown color with shiny hairs. The median area is yellow to orange with small brown spots, while the lateral areas are yellow-brown with brown spots and black streaks.
The eight eyes are in two rows of four.
The flattened abdomen is covered in hairs and is yellow with brown markings. There is a brown medium stripe.
Males are darker with fewer patterns.
Their long legs are yellow with fine brown to black spots.
Brown Recluse vs Red Running Crab Spider
- Yellow/brown cephalothorax covered in hairs with the median area covered in tiny spots
- Eight eyes arranged in two rows of four
- Flattened and hairy abdomen in yellow with brown markings and a brown median stripe
- Speckled legs in yellow with black or brown spots
15. Schizocosa mccooki

This is a large brown spider with a dark diamond shape over the cardiac region. The females can grow to 22mm in body length, with males being smaller at 15.5mm in body length.
They are common in California and the western half of the United States.
Brown Recluse vs Schizocosa mccooki
- Large diamond shape on cardiac region
- Larger than brown recluse
- Common in California
- No violin marking
16. Lance Wolf Spider
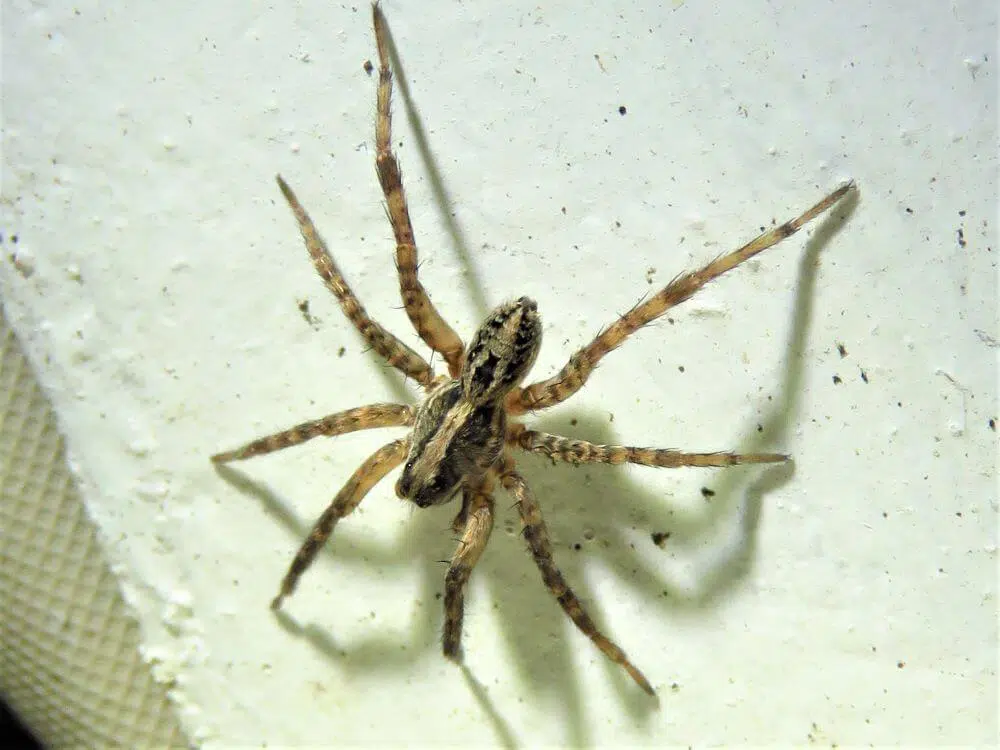

Scientific name: Schizocosa avida.
Common name: Lance Wolf Spider.
The lance wolf spider can be found throughout the United States, though they are more common in the Eastern regions.
They are often found in backyards, meadows, fields, and pastures where they hide during the day.
They are large spiders growing to two inches, or more in leg span. Their legs are gray, brown, or yellow without any banding.
Their light brown body has a blond stripe down the carapace, ending at the abdomen, where it becomes two stripes surrounding a dark lance-like marking.
Brown Recluse vs Lance Wolf Spider
- Light brown body with a light stripe down the carapace
- Two stripes with darker lance-like marking on the abdomen
- Eight eyes
- Legs can vary from brown or yellow to gray without any banding
17. Schizocosa crassipes

This is a common wolf spider found in North America that is brown to black in color and often confused with the brown recluse. The tell-tale sign is the thick white stripe that runs down the length of their body. They also have banding on their legs with white “feet.”
Brown Recluse vs Schizocosa crassipes
- Thick white stripe running down the length of the body
- White feet
- Banding on legs
- No violin shape on the cephalothorax
18. Rabid Wolf Spider

Scientific name: Rabidosa rabida.
Common name: rabid wolf spider.
The rabid wolf spider can be easily identified for the two dark stripes o the cephalothorax and the one stripe of the same color on the abdomen. The base color is yellow with females being larger than the ales. They have eight eyes in two rows of four.
Brown Recluse vs Rapid Wolf Spider
- Two dark stripes on the cephalothorax
- One stripe on the abdomen, the same color as the stripes on the cephalothorax
- No violin marking
- Eight eyes in two rows of four
- Yellow base color
19. Tigrosa annexa

There isn’t much information regarding this wolf spider, which is common in eastern North America. They are often confused with the brown recluse due to their coloration and size. The one difference is that the Tigrosa annexa has a light stripe that runs the center of the body.
Brown Recluse vs Tigrosa annexa
- Light stripe down the center of the body
- Found in eastern North America
- No violin marking on cephalothorax
20. Wetland Giant Wolf Spider
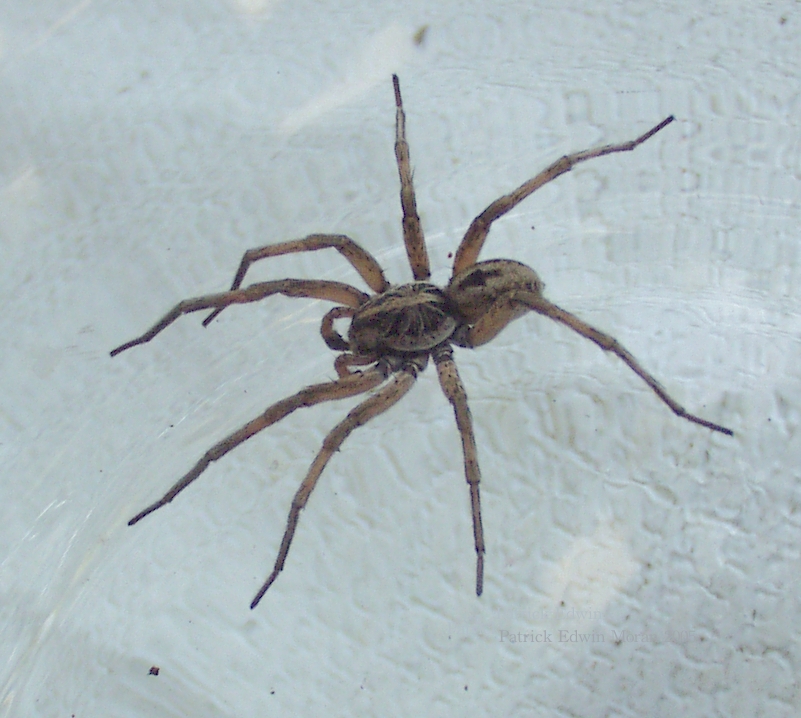

Scientific name: Tigrosa helluo.
Common name: Wetland giant wolf spider.
The wetland giant wolf spider is a large spider that can grow to 1.38 inches (35mm) in body length. The eight eyes are arranged in three rows.
These spiders rely on camouflage to protect themselves against predators, therefore their color is based on their favored habitat. Many are a solid brown.
They are often found in homes when males accidentally wander into the home looking for a mate.
Brown Recluse vs Wetland Giant Wolf Spider
- The wetland giant wolf spider is larger than the brown recluse
- Their coloration varies on their habitat, though many are solid brown
- No violin-shaped marking on their cephalothorax
21. Tigrosa georgicola

This spider belongs to the Lycosidae family and is found in the southeastern parts of the United States.
Adults can grow to 0.86 inches with females being larger than males.
The tigrosa georgicola is brown with a light brown stripe in the center of the carapace and lighter markings on the abdomen.
Brown Recluse vs Tigrosa georgicola
- Brown coloration with a light brown stripe in the center of the carapace
- Light markings on the abdomen
- The violin-shaped marking on the cephalothorax is missing
22. Northern Yellow Sac Spider

Scientific name: Cheiracanthium mildei.
Common name: Northern yellow sac spider.
The Northern yellow sac spider has a green or tan body with dark brown chelicerae and palpi.
They can grow to 10mm in body length with the legs ending in a double claw and the front pair of legs being double the size of the rest of the legs.
These spiders can and will bite, but their bite is not considered a medical emergency.
Brown Recluse vs Northern Yellow Sac Spider
- Green to tan-colored body
- Dark brown chelicerae and palpi
- Legs end in a double claw
- Front legs double the length of the other legs
23. Pantropical Huntsman Spider

Scientific name: Heteropoda venatoria.
Common name: Pantropical huntsman spider, giant crab spider, cane spider.
The Pantropical huntsman spider has eight eyes in two rows of four. They are large spiders and can grow to 11.8 inches (30cm) in leg span.
They are a mix of brown or gray with black and white bellies with red patches on the mouth parts. They have prominent spines on the legs and smooth fur on their bodies.
Brown Recluse vs Pantropical Huntsman Spider
- The Pantropical huntsman spider is considerably larger than the brown recluse
- Eight eyes arranged in two rows of four
- Bodies are a mix of brown or gray
- Belly is black and white
- Mouth parts are red
- Spines on the legs
- Fur o the body
24. American Nursery Web Spider

Scientific name: Pisaurina mira.
Common name: American Nursery Web Spider.
The American nursery web spider has a long abdomen with eight eyes arranged in two rows of four. The first row is straight, the second row is in a U shape. They have a dark median band on the abdomen with two rows of spots.
Brown Recluse vs American Nursery Web Spider
- Eight eyes in two rows with a straight first row and U shaped second row
- Dark median band on abdomen with two rows of spots
- No violin marking o the cephalothorax
25. Six-spotted Fishing Spider

Scientific name: Dolomedes triton.
Common name: six-spotted fishing spider, dock spider.
The six spotted fishing spider is large and distinctive.
They have a gray to brown body with eight eyes. There is a pale cream or white stripe running down both sides of the cephalothorax. The abdomen has light spots and lines that run down the sides there are six dark spots under the cephalothorax.
Females can grow to 20mm in body length and 60mm in leg span with males being smaller.
Brown Recluse vs Six Spotted Fishing Spider
- Six spotted fishing spider is large with a gray to brown body
- Eight eyes
- Pale cream to white stripe that runs on either side of the cephalothorax
- Light spots and lines on the abdomen
- Six dark spots under the cephalothorax
26. Dark Fishing Spider

Scientific name: Dolomedes tenebrosus.
Common name: dark fishing spider.
The dark fishing spider can grow to 26mm in body length for females and 13mm in body length for males. Their leg span can reach 90mm.
They are pale brown to dark brown with chevron marks. They have light banding on the legs.
Brown Recluse vs Dark Fishing Spider
- The dark fishing spider is pale or dark brown with chevron markings
- Legs have light banding
- No violin on the cephalothorax
27. South American Toothed Hacklemesh Weaver

Scientific name: Metaltella simoni.
Common name: South American toothed hacklemesh weaver.
This spider can grow to 9mm in body length and is brown with dark sections. The carapace, the end of the legs, and the chelicerae are all darker brown. The abdomen is mottled in gray black or gray with pale chevrons near the back.
Males have orange or yellow towards the carapace that darkens to brown in the front.
Brown Recluse vs South American Toothed Hacklemesh Weaver
- Brown base color with darker sections, such as the carapace, legs, and chelicerae
- Mottled abdomen in gray or gray/black with pale chevrons
- Males have orange to yellow on the carapace
- No violin markings
28. Wall Spider

Scientific name: Oecobius navus.
Common name: Wall Spider.
Wall spiders are small spiders that grow to around 3mm in body length. They are light gray in color with rounded legs. They are known for building flat webs under rocks, in wall corners, and along ceilings.
Brown Recluse vs Wall Spider
- Wall spiders are considerably smaller than the brown recluse
- Light gray in color
- No violin markings on the cephalothorax
29. Cithaeron praedonius

This spider is a yellow to green color with brown markings, belonging to the Cithaeronidae family.
They are common indoors during January and are completely harmless to humans.
Brown Recluse vs Cithaeron praedonius
- Yellow to green in color with brown markings
- No violin shape on their cephalothorax
- The Cithaeron praedonius is harmless to humans
Brown Recluse Bite
The brown recluse is known for its venomous bite and if bitten, you should seek medical attention immediately.
They will only bite if disturbed, such as caught in bedding or clothing.
Ninety percent of the bites from brown recluse spiders heal without any scarring, though the reaction varies from one person to the next, determined by how much venom the spider has injected, along with the person’s sensitivity levels.
In most cases, a bite can leave a red mark which will disappear on its own. For those with high sensitivity, a blister may appear at the bite site, the tissue becomes hard and the lesions become blue-gray patches with ragged-edged.
In severe reactions, the bite can create a volcano lesion, where the damaged tissue becomes gangrenous, leaving an open wound, which can take eight weeks or more to recover from.
Bite Symptoms

Bite symptoms from a brown recluse bite usually develop within the first or second day after being bitten. These symptoms can include:
- Redness and pain at the bite site
- An ulcer forming at the bite site, the skin at the center of the site will turn purple
- Chills
- Fever
- Nausea
- Weakness
- Very rarely people may experience seizures or a coma.
Bite Treatment
It is imperative to see a doctor immediately if you suspect a child has been bitten by a brown recluse, as their small bodies are not able to ward off the effects of the venom.
If an adult is bitten, most can treat the bite symptoms at home. Ten percent may experience ulcers or blisters that cause damage to the skin, requiring medical attention.
If you are experiencing mild symptoms, you can try:
- Cleaning the bite site with soap and water
- Apply an antibiotic cream
- Ice the area to reduce redness, swelling, and pain
- Take over the center pain medication
- Keep an eye out for symptoms getting any worse
If you notice any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately:
- A blister or ulcer has formed at the bite site with a blue, black, or purple center
- The pain of the bite is extreme
- The bite site becomes infected
- You are experiencing problems breathing

Why Causes the Brown Recluse to Bite
Before looking at what causes the brown recluse to bite, it’s important to note that they are not aggressive.
Bites only cause when they are trapped, usually when they are hidden in shoes or clothing and come into contact with the sin.
They hide during the day, coming out at night to hunt for their next meal.
How to Reduce The Risk of Being Bitten by a Brown Recluse Spider
- Remove any clutter from your attic, basement, and yard
- Do not stack wood near the home
- Do not leave clothing on the ground
- Shake clothing before putting on
- Wear gloves when working in the garden, when moving wood or rocks
- Be wary when removing things from storage, brown recluse spiders enjoy hiding in cardboard boxes
- Always check inside your shoes before putting them on
- Store your handheld outdoor equipment and tools in sealed plastic bags
Summary
The brown recluse is not an aggressive spider and will try and flee rather than be aggressive towards a human.
Bites do occur, normally when you put on shoes or clothing and get the spider stuck between the clothing and your skin.
Being able to quickly identify the brown recluse can ensure you receive the proper medical treatment you need.
The brown recluse has a dark violin shape marking on the cephalothorax with six eyes which are arranged in pairs. They have light-colored legs without the banding.
Further Reading: