Tarantulas are spiders that are very easy to identify with their large size and hairy legs and bodies. There are 5 types of tarantulas found in Colorado.
If you see a tarantula in the area, chances are it’s a male as the females never move far from their burrows.
Here are eight facts about Colorado tarantulas from the types to where to find them, along with the tarantula migration, which occurs annually.
1. Type Of Tarantulas In Colorado
There are 5 types of tarantulas that have been reported in Colorado:
- Aphonopelma coloradanum
- Aphonopelma echinum (Colorado chocolate brown tarantula)
- Aphonopelma hentzi (Oklahoma brown tarantula)
- Aphonopelma vogelae
- Aphonopelma marxi (Grand Canyon black tarantula)
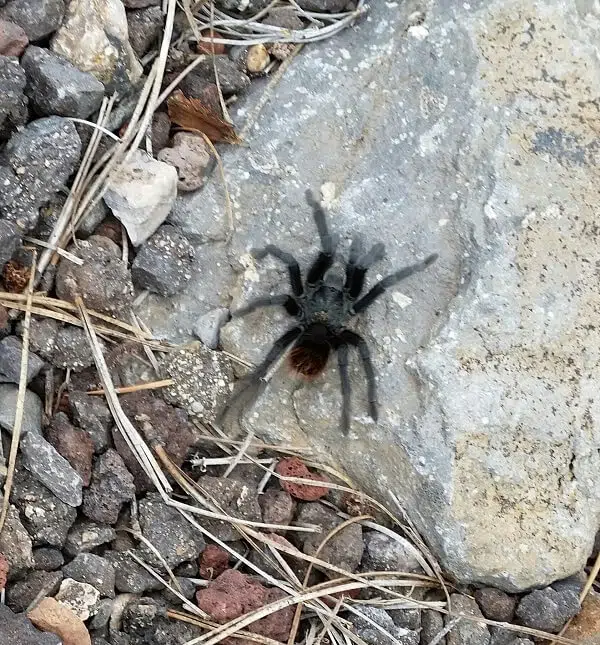



They are large and hairy with all species in Colorado ranging from black to dark brown. The belly hairs are sometimes slightly lighter than the rest of their bodies. Most have banding on their legs.
The majority of those observed are males which are migrating to find early fall and late summer.
Females, if observed, will not be far from her burrow. She looks similar to the male, but females don’t have long legs, even though they are larger in size.
Further Reading:
2. What Do Colorado Tarantulas Eat?
The Colorado tarantulas are all nocturnal and hunt at night. They stay close to their burrow and wait for prey to pass. Once the insect is within a few inches, the tarantula rushes forward to catch the prey, digging its fangs into it.
They are insectivores and eat a host of beetles and other insects, including grasshoppers and crickets.
It can take a tarantula more than a day to completely finish eating an insect.
3. Are Colorado Tarantulas Dangerous To Humans?
Even though they look scary and large, tarantulas are not normally aggressive and will only bite if provoked. They are usually shy and docile and would much rather run back and hide in their burrow than have to fight you.
They can give a painful bite with their large fangs, but their venom is not fatal to humans.
These are New World tarantulas which gives them hairs on their belly which they kick off in the direction of a threat. These hairs are very irritating if you get them on your skin.
In case of face or throat swelling or rash, which could be an allergic reaction to the bite, seek medical assistance immediately.
Further Reading:
4. Where To Find Tarantulas In Colorado?
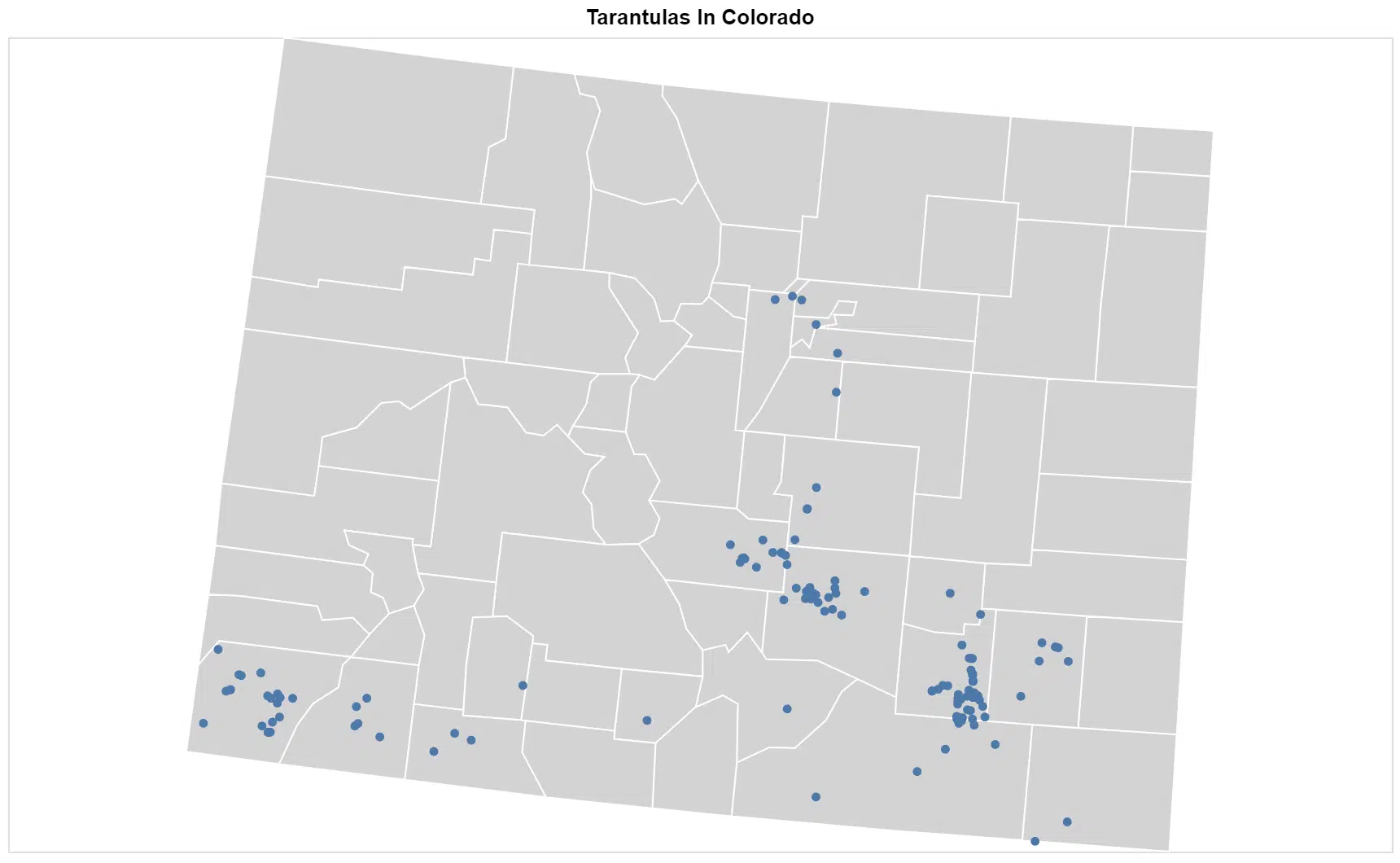
Most tarantulas encounter in Colorado are on the southeastern side, mostly where the counties border the Arkansas Valley. This region is mostly prairie land and not cultivated land, which is not the ideal habitat for these spiders.
Tarantulas live in burrows during the day, sometimes these can be up to one foot deep.
They have a vertical burrow with side chambers, which are all reinforced with silk with dried leaves and a silk web around the entrance to their burrow, which deters predators and helps protect the tarantula as it rests during the day.
5. When To Find Colorado Tarantulas?
Tarantulas are nocturnal, coming out at night to wait for prey to move past their burrow. They seldom move far from their burrows, except when the males migrate. This means that it is very rare to come across a tarantula in Colorado.
If you want to observe them, the majority of observations have been at night, from mid-August through to late September, when the males migrate.
6. Tarantula Migration In Colorado
The annual tarantula migration takes place every fall. This is where large numbers of male tarantulas make their way across La Junta and southeastern Colorado. As the temperatures cool in late summer, these tarantulas start an annual ritual, their migration.
Throughout the year they stay in their burrows, safe from predators. Late summer and early fall, they become more visible with more observations.
The migration usually starts in southeastern Colorado close to the end of August and September. It peaks around October. After the mating season, males tie within a few months.
7. What To Do If You See A Tarantula?
Tarantulas give a very painful bite and the hairs can be very irritating on the skin, which is why you should not pick up a tarantula if you see it, but rather observe it from a distance.
Due to the fact that the female will seldom leave her burrows and males only move away from their burrow during mating season, it is not that common to find one in the home. If you do find a tarantula, rather capture it safely without harm and release it back into the wild.
8. Safety Precautions
There are a number of safety precautions you can bear in mind when you see a tarantula or encounter one in your home.
Do Not Handle
Tarantulas should not be handled. If you do decide to handle one of these inverts, then you need to do so only if very necessary, such as moving them from inside the home.
Remember that if you choose to handle one of these tarantulas, they do have defensive toxins which can cause an allergic reaction.
If you are pregnant, a child under five has been bit tenor a senior citizen, then seek medical treatment.
Do Not Provoke
Tarantulas are shy and nervous, but they will bite if provoked and their bite is venomous and can result in an allergic reaction.
It is important never to provoke these spiders to reduce the risk of venom exposure.
They do not only have a painful bite, but they have hairs on their belly, called urticating hairs, which cause irritating and itching. The hairs work their way into the skin, which also can result in an allergic reaction.
Clean the Area
In the event, you accidentally provoked a tarantula and ended up full of itch-causing hairs or a bite, wash the area immediately with antibacterial soap and hot water. Use the hottest water you can to neutralize the venom.
If you have hairs on you that are causing irritation, wash the area and do not touch your face or eyes. Seek medical help to remove the hairs effectively.
Summary
The tarantulas you may encounter in Colorado are not harmful to humans, as long as you observe them from a distance and don’t provoke them.
The 5 species are all very similar that it is almost impossible to tell them apart.
They are all easily identifiable, nocturnal, and docile. If you find one in your home, remove it carefully, releasing it back into the wild.
Further Reading: