Some of the most colorful tiny bugs in homes and gardens are yellow. Vivid yellow coloring makes these bugs stand out more than brown or black bugs.
Some of the friendliest-looking bugs are also yellow, which is the case with yellow ladybugs.
Other bugs might appear yellow and friendly, but they can be real pests eating up flowers, and vegetables, and attracting predatory bugs to your home.
Some yellow bugs can be pests while others can be beneficial by eating common pests.
Beneficial yellow bugs include yellow ladybugs and yellow ants such as Yellow Meadow Ants.
Both of these beneficial species eat detrimental bugs such as aphids which can eat grass, vegetable leaves, flowers, and tree leaves.
Other yellow bugs such as chiggers or head lice are problematic as they bite and feed on human blood.
These bugs tend to be picked up by someone carrying them or simply by taking a walk out in nature in tall vegetation.
Indirect damages can also be detrimental to humans by economic loss. Yellow bugs such as dampwood termites can also be a considerable problem to homes already affected by water and humidity.
Termites cause further damage to homes affected by water.
The following bugs are either beneficial or detrimental. All of these species are common around homes.
1. Aphids – Tiny Yellow Bugs on Plants
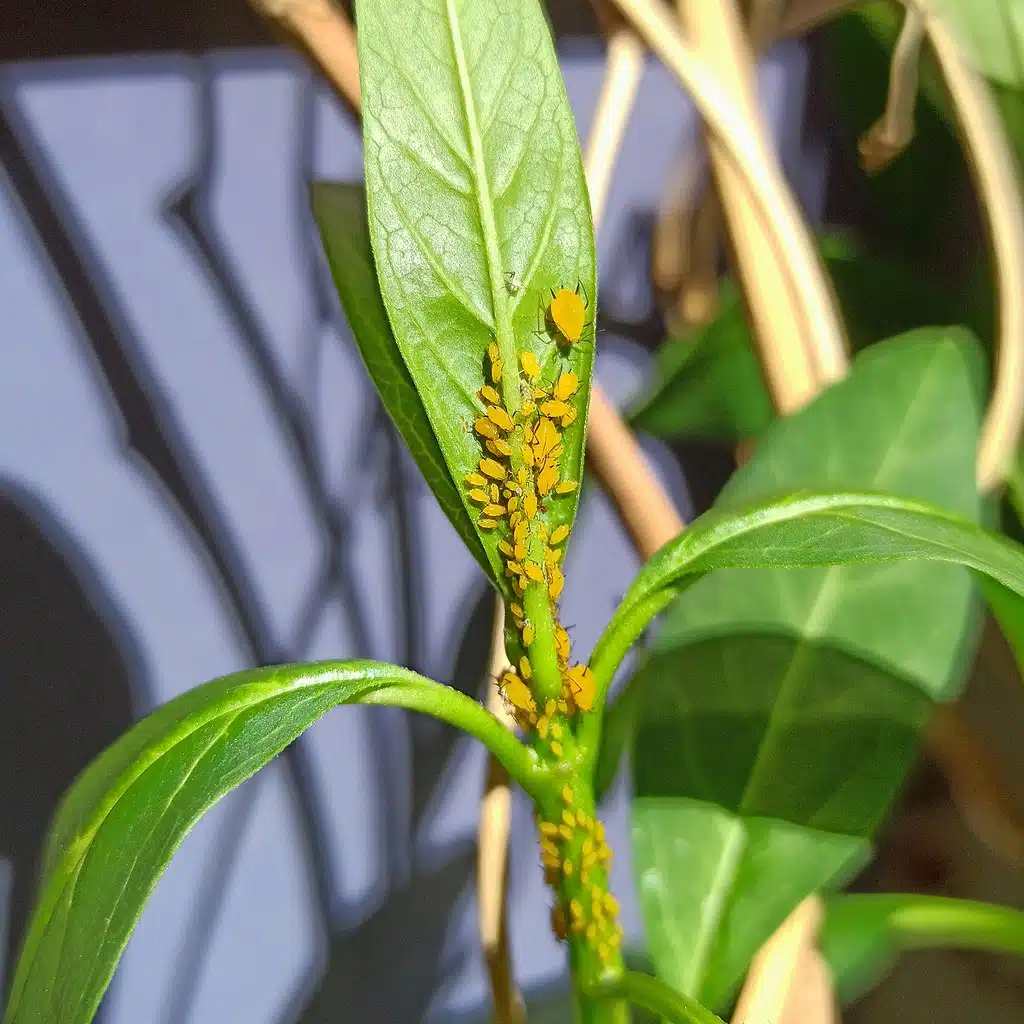

There are thousands of aphid species on crops and gardens. Yellow aphids might not be as widespread as green or red aphids.
Species such as the Oleander aphid (Aphis nerii) are among the most common species of yellow aphids in North America.
This imported species doesn’t impact fruits and vegetables in the garden as it prefers to eat milkweed.
In most parts of the world, this Mediterannean-origin aphid doesn’t create large problems for its host plant.
Most damages inflicted by aphids don’t kill their host plant.
Aphids produce honeydew which is only problematic in high amounts as it remains somewhat of a minor problem for host plants.
Honeydew also attracts ants, one of the larger problems whenever these aphids impact plants in your garden.
Numerous small yellow Oleander aphids can even kill milkweeds by eating the sap in the plant’s leaves.
This reduces the food choices of many species of butterflies, caterpillars, ants, and other insects that commonly feed on milkweed.
You can remove yellow aphids from plants and vegetables in the garden by hand. These bugs might eat up plants but they cannot bite and they are safe to maneuver.
2. Thrips – Tiny Yellow Bugs on Skin
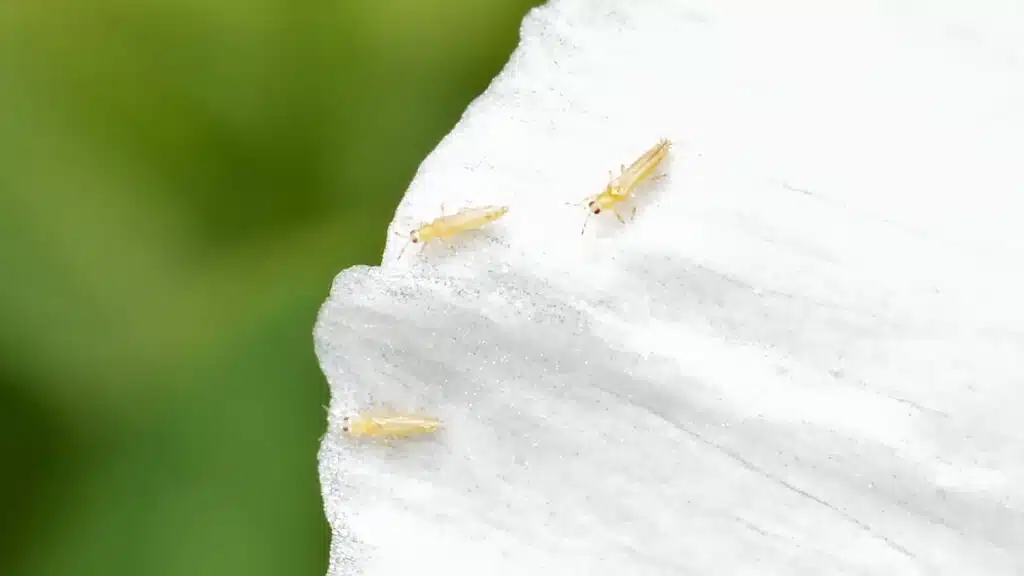

Thrips are mostly known for their brown or green coloring. These plant-feeding insects with their elongated bodies are often seen on plants in the garden.
Yellow thrips are a frequent sight on strawberries. These tiny yellow insects feed on strawberries with different results.
Most thrips are too small or live in reduced numbers to cause significant plant damage.
On the other hand, strawberry crops can be highly impacted by thrips.
One of the most detrimental habits of thrips is their capacity to eat plant seeds from the flower buds themselves.
Flower bugs open at different moments of spring and summer, depending on the type of strawberry.
Yellow thrips feed on all types of strawberry seeds essentially slowing down or even stopping fruit production.
These colorful thrips can be removed by hand. Essential oils and even water and vinegar are successfully used on strawberries to keep these insects away.
3. Bed Bug Nymphs – Tiny Yellow Bugs in Bed
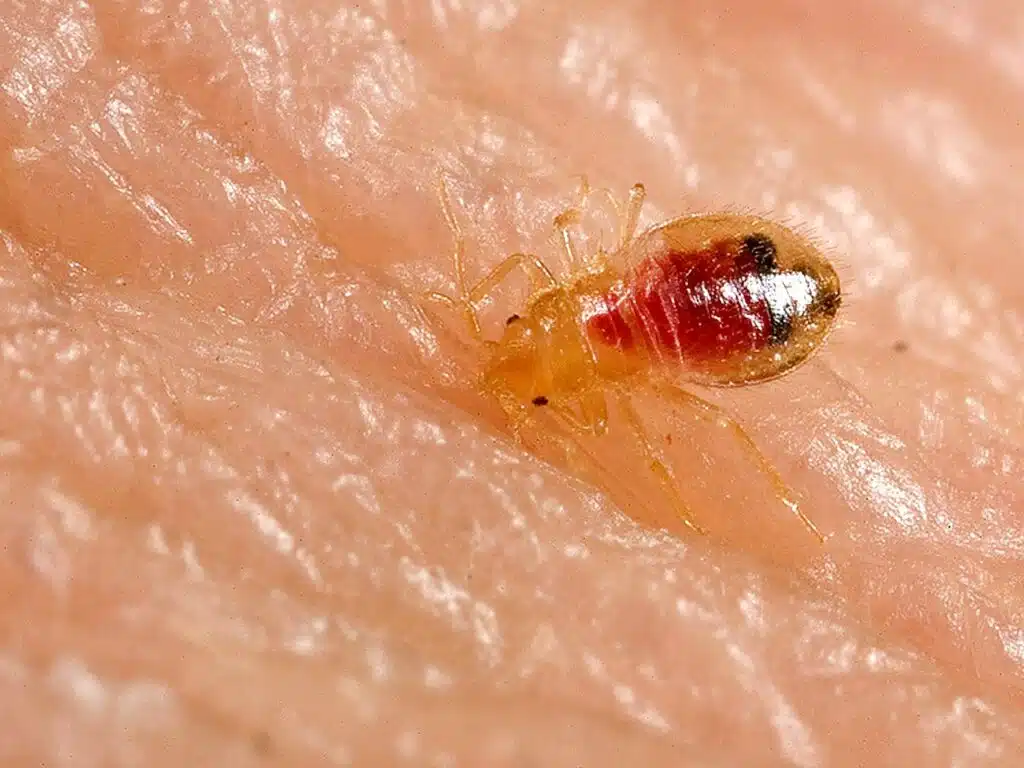

Bed bugs are some of the most common home pests. These types of bugs are yellow when unfed, as nymphs.
Unfed bed bug nymphs are yellow through their 5 instars or growth stages.
Only fed bed bug nymphs are red. Furthermore, even fed bed bug nymphs are partially yellow in the cephalothorax.
Bed bugs nymphs eventually become blood-feeding adult bed bugs.
Similar to seeds in shape and size, these bugs are among the most common home pests, typically found on beds.
You can pick up bed bugs on your clothes from sleeping in an infested bed such as a hotel bed with bed bugs.
Adult bed bugs are easier to spot and stay away from as they have a red color that may have some brown nuances to them.
Nymphs are smaller, yellow, and a bit translucent which makes them more difficult to spot.
A sign of bed bug nymphs is seeing adult bed bugs as their nymphs are found in the same place as the adults.
4. Chiggers – Tiny Yellow Bugs That Bite
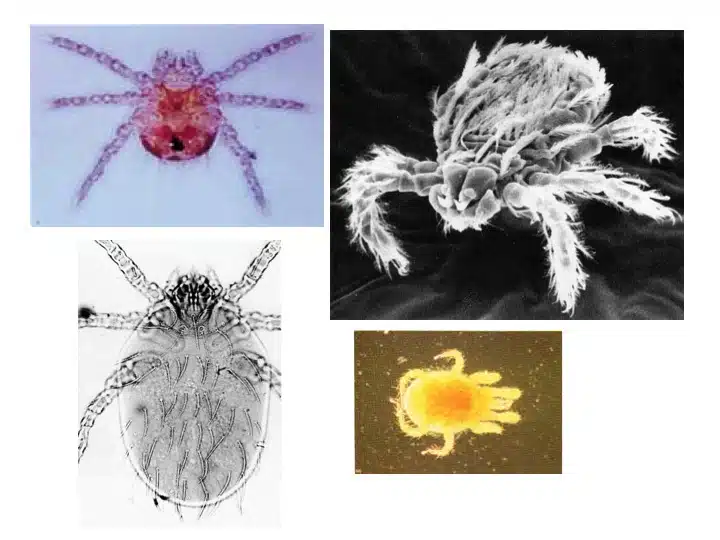
Most common in the spring and the summer, chiggers are among the yellow bugs that are easy to spot.
Chiggers aren’t yellow by default as they only turn yellow once they bite and feed on human skin.
Sometimes difficult to spot individually, chiggers are mostly noticed in small groups whenever clusters of bugs are seen on plants.
The bites of chiggers come with red itchy skin. These symptoms can take days to clear. In more extreme cases, chigger bites take up to 2 weeks to clear.
These bugs are picked up when making your way through tall dense vegetation in the spring or the summer.
Chiggers attach themselves to the skin from vegetation. You may only need to see a doctor in case of complications following the bites.
A common example of chigger bite complications includes infections.
5. Water Mites – Tiny Yellow Bugs in Pool
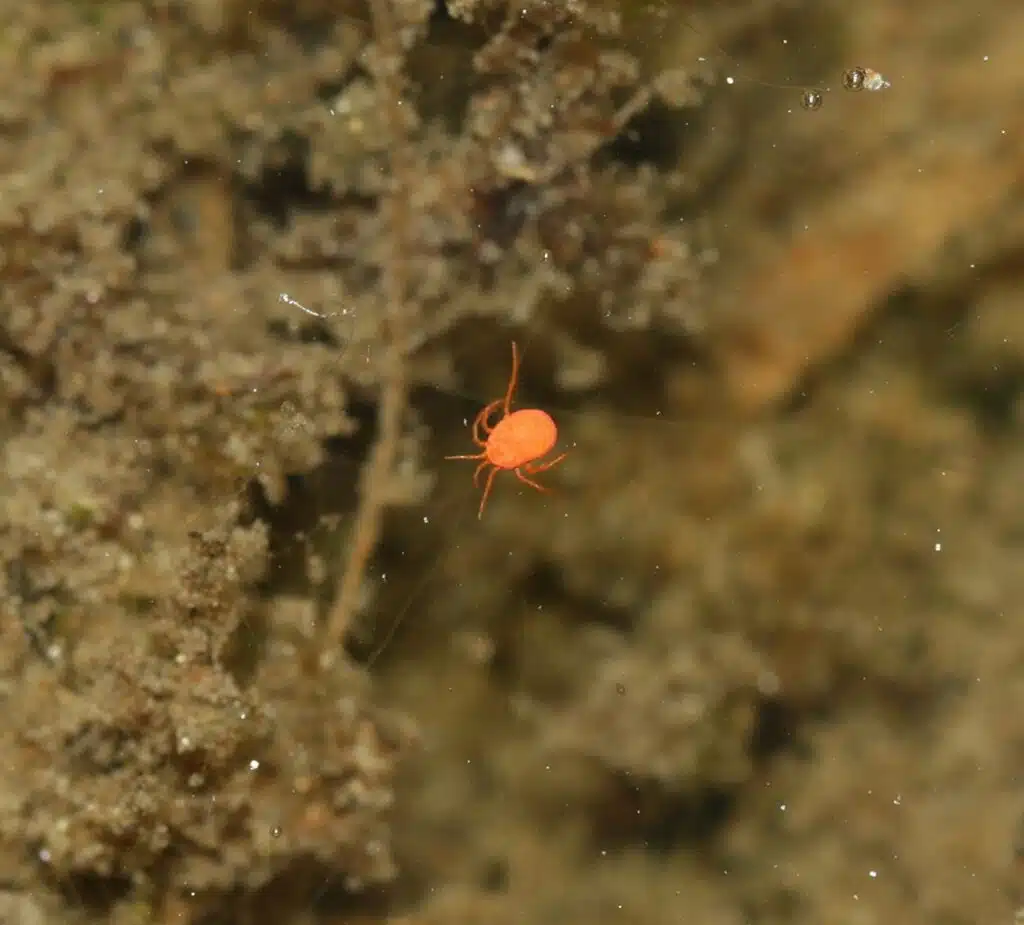

Thousands of species of water mites exist around the world. Their exact number is unknown since these mites are not the object of too many studies.
There are a few yellow or red yellow water mites from the thousands of species known to researchers.
A large number of these water mites are parasitic. They attach themselves to various hosts that live in water.
Some water mites can survive outside water as adults but their larvae are mostly aquatic spending the developing stages of the species underwater.
Mosquitoes are among the most common hosts for the parasitic larvae of water mites.
One or multiple tiny, often microscopic, water mite larvae attach themselves to mosquitoes and other water bugs.
Springs, rivers, and lakes are among the most common habitats for water mites.
6. Head Lice and Lice Eggs – Tiny Yellow Bugs on Hair
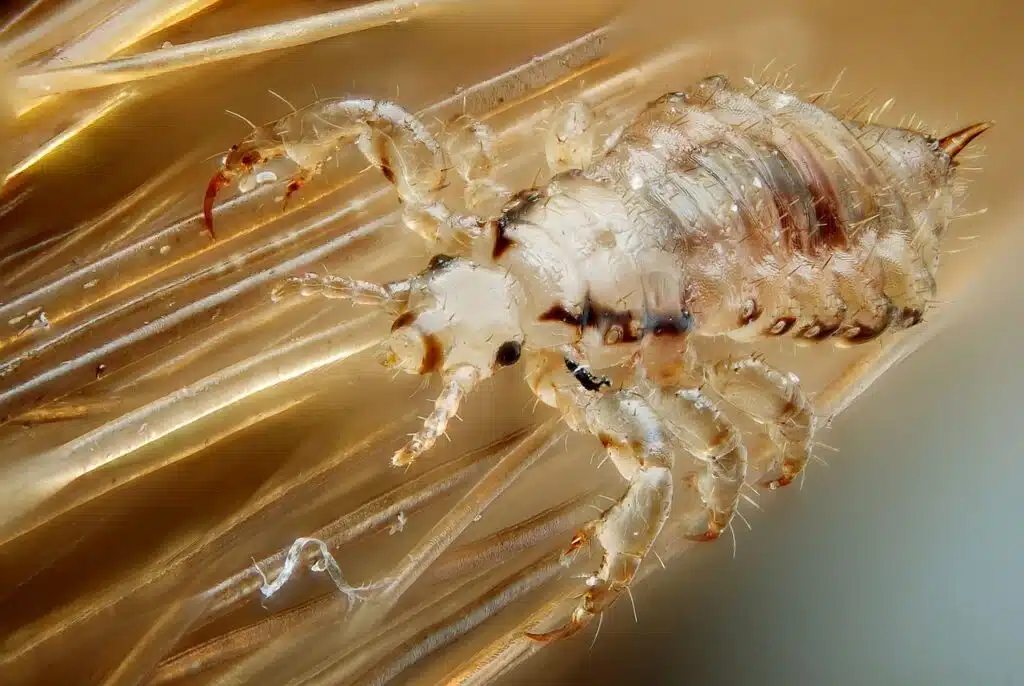

Head lice and lice eggs can be yellow. Some of the most problematic yellow head lice are seen in children and teenagers.
Head lice grow up to a maximum size of 0.3mm which means they can be difficult to spot. Their eggs are also similarly small.
Consuming small amounts of blood, head lice are some of the most problematic yellow bugs as they are difficult to eliminate.
While special shampoos have proven efficient, it takes more than washing the hair with a good shampoo to eliminate head lice and eggs.
Washing all clothes, and bed sheets, and cleaning up entire rooms or homes are advisable when it comes to eliminating head lice.
One of the first signs of head lice is a tickling sensation. You find this sensation is only specific to the head.
It’s important to check for head lice as tickling sensations are also specific to other conditions such as suffering from excessive dandruff.
7. Ladybugs
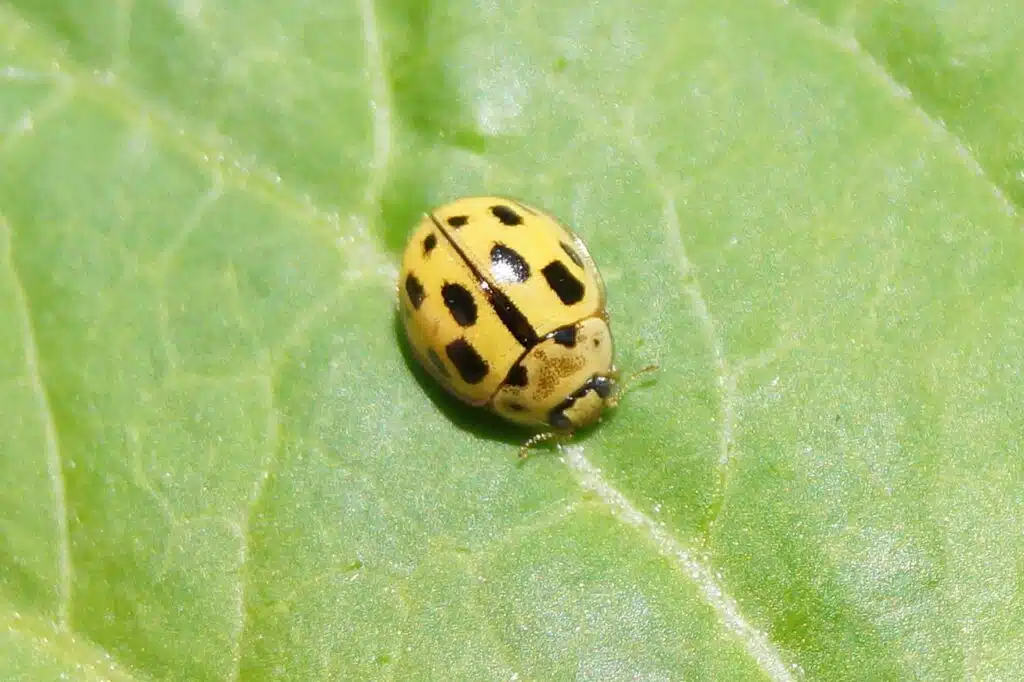

Ladybugs are typically red. However, species such as the Fourteen-Spotted Beetle and the 22-Spot Ladybug are mostly yellow.
These bugs have yellow elytra which are shaped like a dome, similarly to other ladybugs.
A bright yellow color is specific to these ladybugs. You can find them in gardens, on crops, or in meadows.
Many yellow ladybugs are predatory species with a beneficial character.
They feed on mites and aphids as well as on all other soft-bodied insects.
As a result, you can find yellow ladybugs in the garden on vegetables or on plants that are consumed by small soft insects.
Yellow ladybugs look for these insects, their larvae, and their eggs for food.
Most yellow ladybugs remain yellow most of their lives. Just a small percentage of these species start to fade in color with time.
Yellow ladybugs share much of their habitats and their food preferences with the most common or popular red ladybugs.
8. Booklice

Booklice are some of the most common tiny bugs that come in various colors and shades. Yellowish color with a slight translucent profile is also specific to this species, asides from the gray color.
Booklice are among the most common small bugs that might not be seen indoors but are likely present in areas with mold and high humidity.
This species eats mold, books, and even small insects.
It damages old books affected by mold or humidity and it also thrives and multiplies in areas of the house with mold formation.
Even the first mold molecules which aren’t visible provide the environment for this species to thrive.
Eliminating booklice is only possible by first eliminating mold, fungi, and high indoor humidity.
Many booklice retreat in areas that still have some humidity left such as on bookshelves where they feed on the glue that keeps book pages together.
Booklice can cause mild allergies, as does high indoor humidity. Eliminating them can also eliminate one of the main causes of respiratory allergies.
9. Fleas
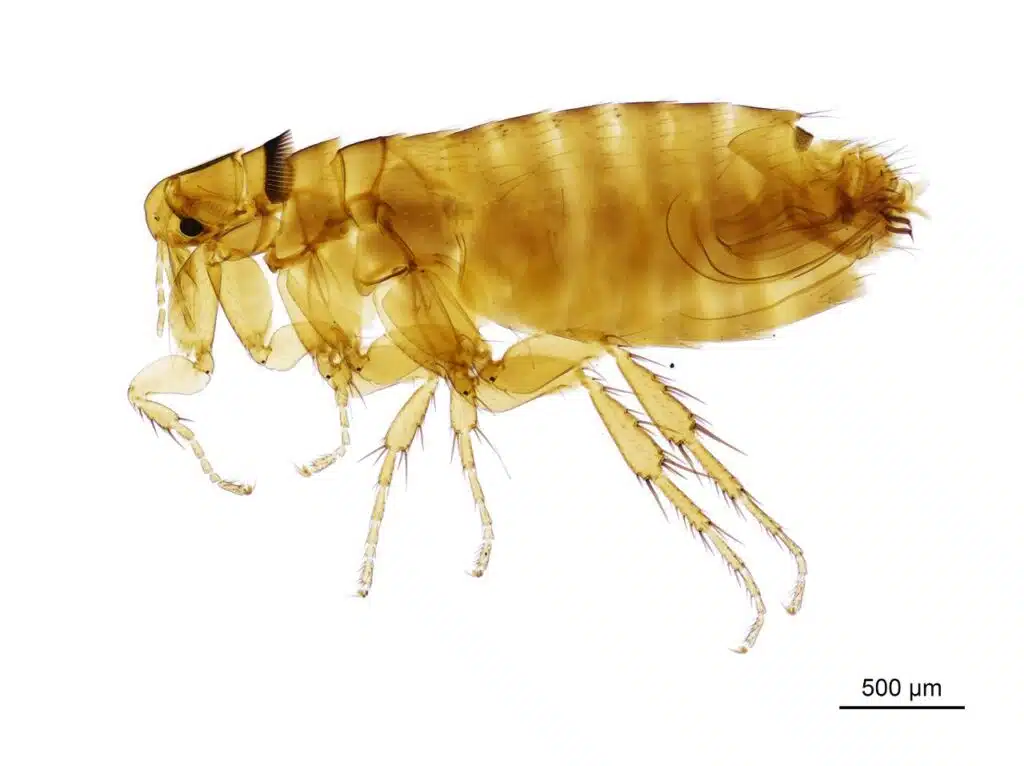

Insects of the Siphonaptera genus known as fleas have yellow larvae and a yellow body when unfed.
Fleas are sometimes too small to be immediately noticed when unfed. They are colored to a dark red or brown body color soon after a blood meal.
Fleas can measure only 2-3mm which makes them difficult to spot at first. They tend to attach themselves to a host such as a pet or a human for food.
Feeding on blood, fleas can cause significant rashes, skin irritation, or even skin-level infections.
You can catch fleas from walks out in nature, from pets, or from getting in contact with other infested animals.
Fleas can also make their way to a human host from other people carrying them.
Homes with pets or homes that are in proximity to animals are often the most exposed when it comes to fleas.
Removing fleas is subject to washing yourself properly either with soap and water or with a special shampoo.
Fleas eventually die if they cannot find a suitable host. They need blood to survive and their lifespan is reduced without an animal such as a dog or a human as hosts.
10. Springtails
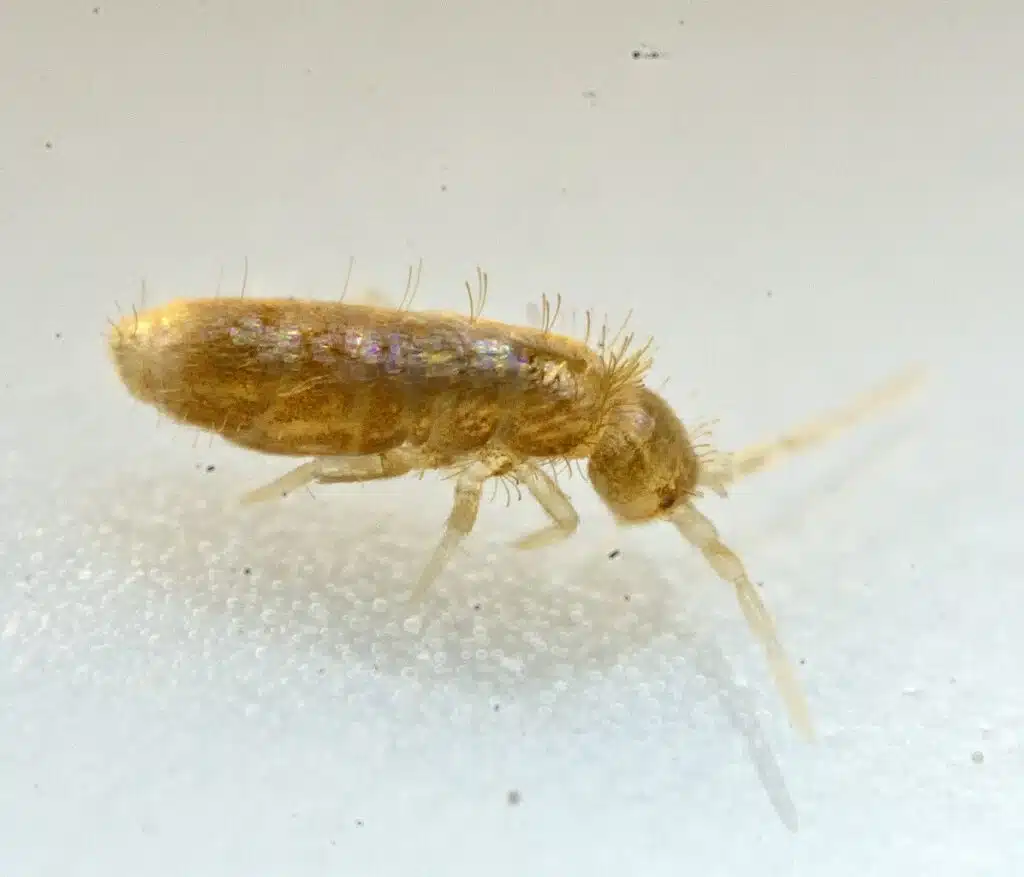

Springtails have small elongated yellow bodies, yellow heads, and yellow legs.
Most commonly, springtails are found around the house or in the garden.
These small yellow bugs feed on decaying organic matter. Decaying leaves, plants, and even decaying fruit might represent a type of food springtails are interested in.
You can find springtails all around the backyard. This includes areas such as tree bark or dead leaves. Most easily, you can uncover springtails under a rotting log or a rotting piece of wood that’s been sitting out in the rain for a long period.
These bugs don’t bite but they can make it indoors with various plants.
Carrying or hosting large potted plants inside of the house can favor the appearance of these bugs.
In turn, soft-bodied springtails might also attract other predatory insects.
11. Ants
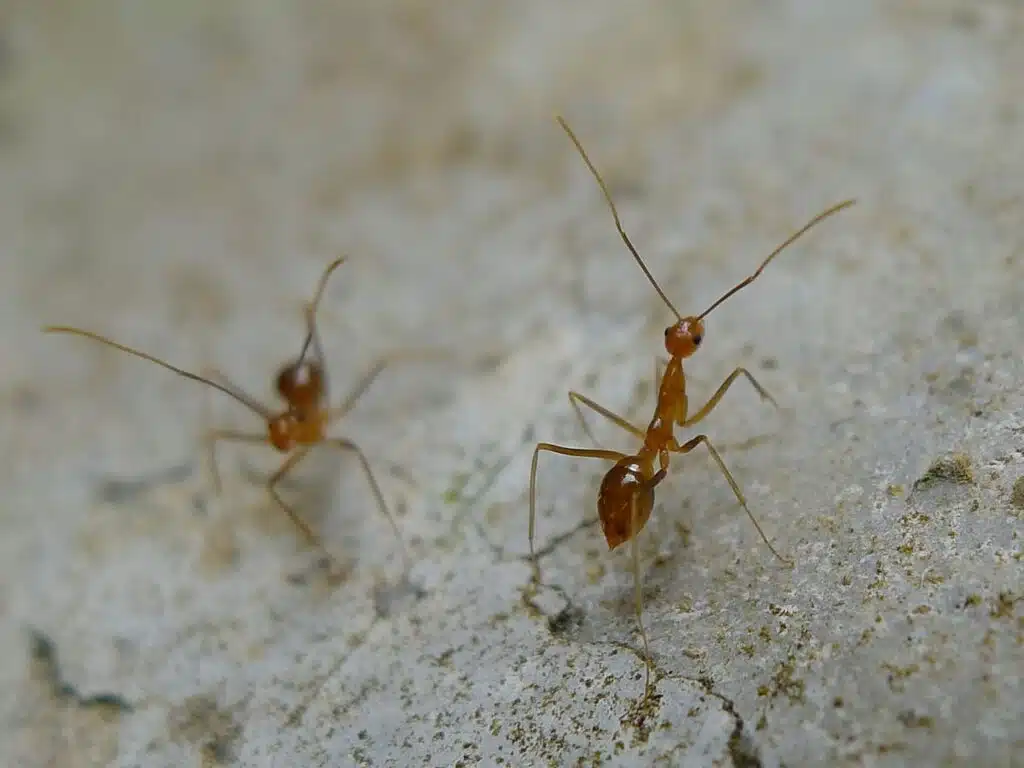

Ants are known for having either a red or brown color. However, yellow ants also exist in certain parts of the world.
Yellow Crazy Ants are some of the most common yellow ant species. These ants have an uncertain origin.
Some say Yellow Crazy Ants come from West Africa while others say they have an Asian origin.
Australia is one of the countries that have a very large Yellow Crazy Ant population.
Feeding on all types of underground insects, these ants can be difficult to control and eradicate.
Also feeding on seeds, these ants spend most of their lives underground, which also explains their pale or pale-yellow color.
Yellow Meadow Ants (Lasius flavus) are another common species of ants that are yellow.
The soil under the lawn is the most likely place to find these ants around the house. Yellow Meadow Ants feed on the honeydew of aphids which eat grass roots.
They have almost no impact on the lawn itself.
However, these ants may have a positive role in the health of your lawn as they can turn to eat aphids in the cold months.
Yellow Meadow Ants are some of the most important aphid predators.
12. Termites
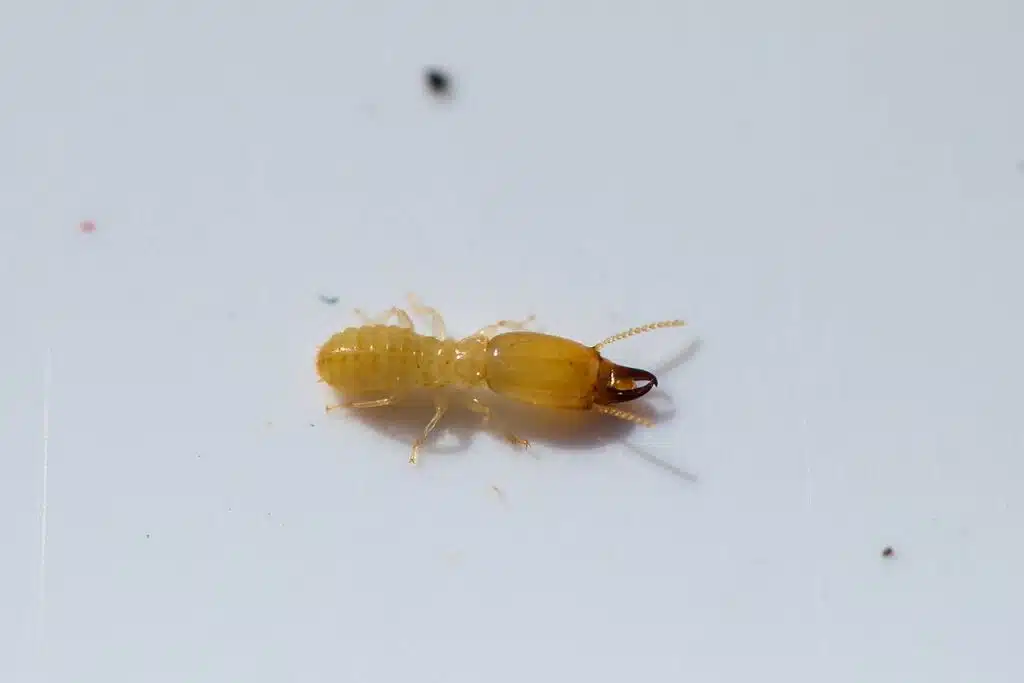

Dampwood termites have a pale or yellow color.
These termites come in different casts and sizes. Soldier dampwood termites grow to a maximum length of 20mm.
As their name implies, these types of termites are only interested in building colonies in dampwoood or wood that’s been in contact with water for a long time.
Soft fibers easy to chew through represent one of the main reasons these termites prefer wood that’s been affected by water for shelter.
Wooden structures built directly on wood in areas known for hosting termites tend to be the most exposed.
Even structures built on solid foundations can be impacted by dampwood termites.
High indoor humidity or water leaks can lead to direct wood-water contact which creates the ideal habitat for termites.
These termites can either fly towards the impacted wood or make their way from the ground to the wood.
You can find these types of termites in old homes affected by water leaks.
Most commonly, you can find these termites in rotting wood or logs that have been sitting out in the rain for years.
13. Yellow Flies
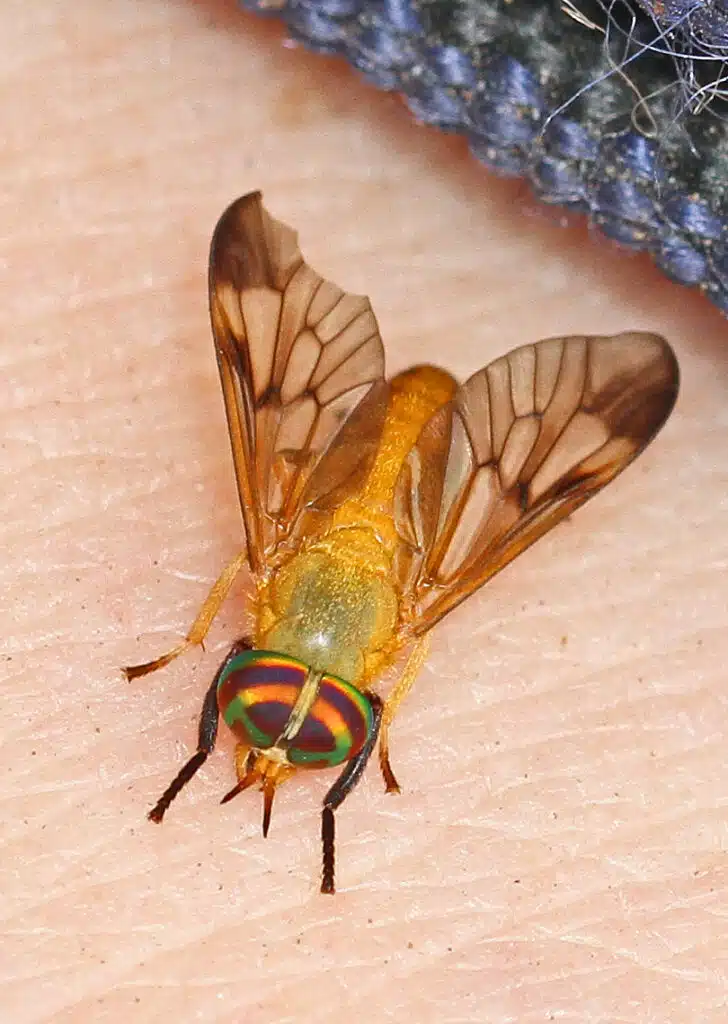

This species of flies (Diachlorus ferrugatus) encompasses multiple subspecies of yellow flies specific to subtropical regions such as those in Florida.
Growing to a maximum size of 0.4 inches, these flies commonly have a shiny dark yellow body, a green head, and transparent wings.
Multiple types of Yellow flies are seen in the spring and the summer.
These flies are mostly known for feeding on nectar and pollen but females can bite.
Male flies exclusively feed on plant nectar and pollen while females need a blood meal to lay eggs.
Female yellow flies are distinguished from males by their short distance between the eyes. These details aren’t seen without magnification so it’s best to stay away from all Yellow flies.
The result of an unwanted encounter is a bite.
The bites of Yellow Flies are considered moderately to highly painful.
Red skin, swollen skin, and itchy skin are all common symptoms of a Yellow Fly bite.
These flies can make it indoors through open windows or around doors and windows making the most of tiny gaps.
While they can live and survive their whole life indoors, these flies aren’t the subject of any direct management solution.
There’s no chemical or repellent specifically used against Yellow Flies.
Some of the most efficient solutions to keep Yellow Flies away involve applying mosquito spray on yourself before heading out.
14. Stink Bug Nymphs
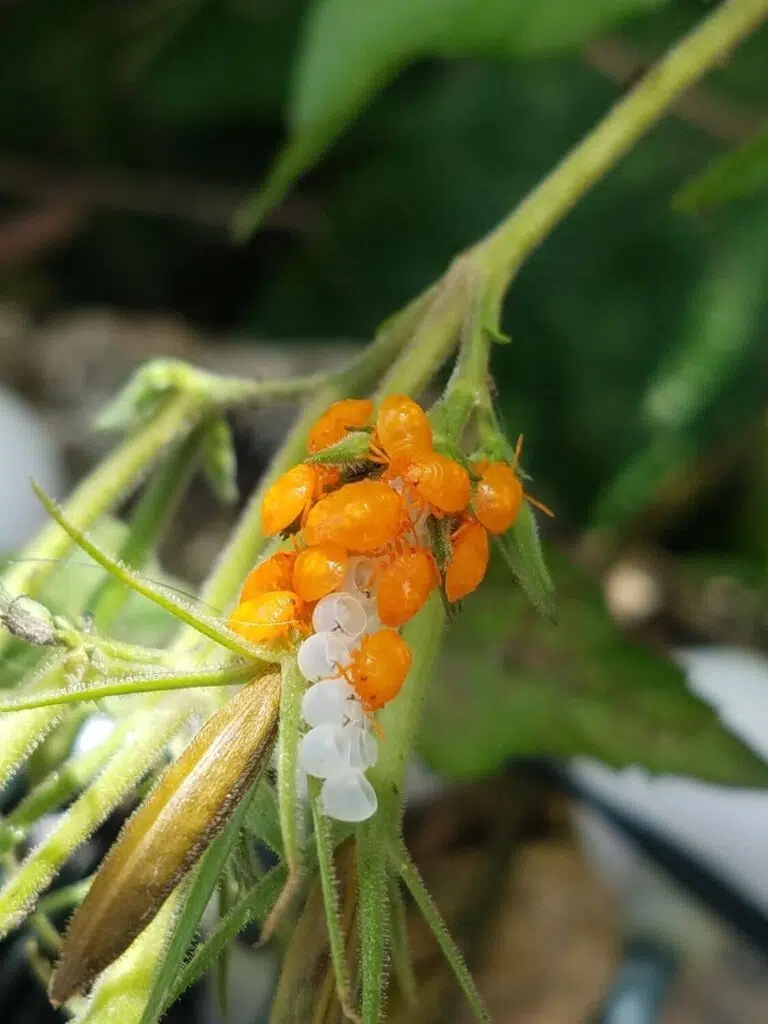

Stink Bugs are some of the most common bugs that feed on plants in North America.
Known for their shield-like body shape, these types of bugs are native and come from many species.
While not yellow as adults, they begin life as small yellow bugs.
Stink Bug Nymphs often begin life as yellow and black or yellow and brown nymphs.
Small but still visible, these nymphs are seen on various leaves around the garden. They feed on leaves and plant stems.
You can find Stink bugs and their nymphs around the garden until late fall, depending on the season.
Apple trees are some of the most common hosts for these types of bugs and their nymphs.
Berries are also a host plant for the species together with legumes such as beans.
The damages of these nymphs are generally small but can be considered in small gardens and on crops.
Nymphs tend to grow together on a single host plant as adults lay eggs in clusters on a single plant.
This means these small colorful yellow nymphs can halt the growth of their host plant.
Yellow Stink Bug nymphs go through 5 instars before becoming adults and changing their food preferences.
15. Spotted Cucumber Beetle
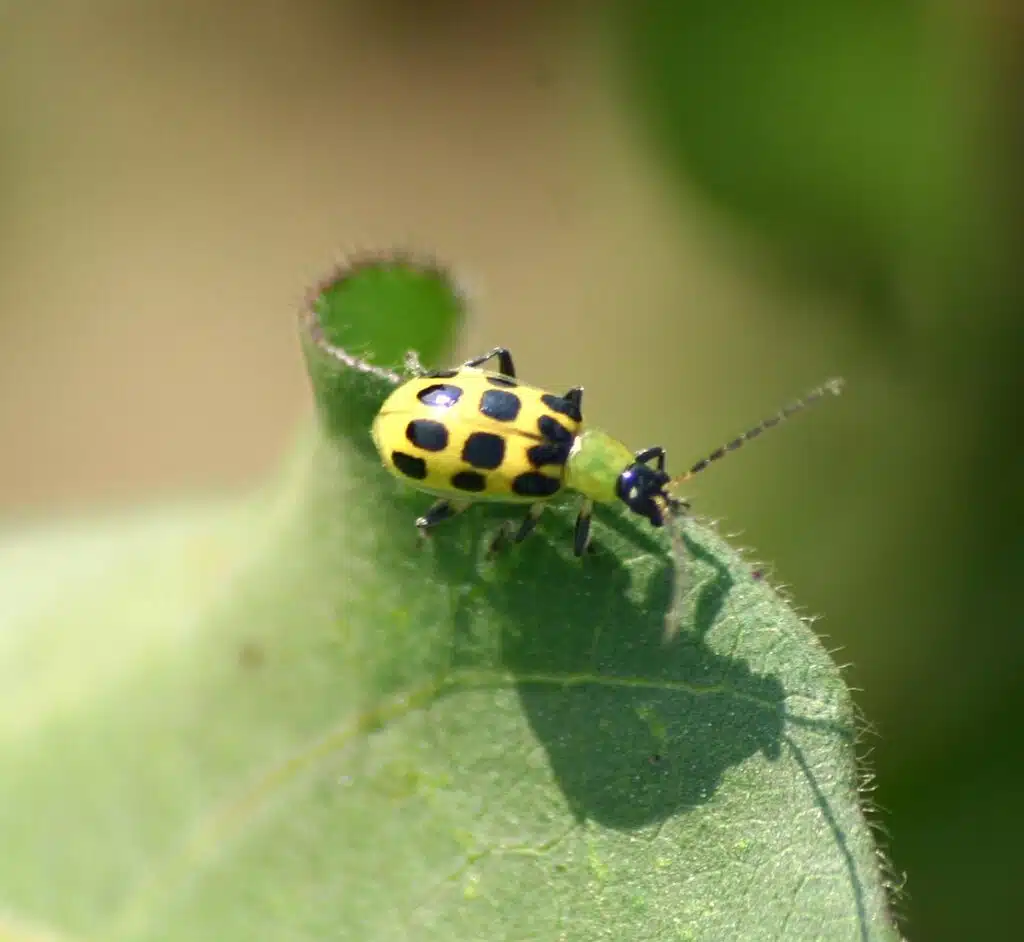

Spotted Cucumber Beetles (Diabrotica undecimpunctata) are mostly yellow bugs that feed on various parts of cucumber plants.
This species has yellow elytra decorated with black spots which makes it look poisonous.
Its head is black while the section behind its head can be green or black.
Spotted Cucumber Beetles are some of the most common cucumber pests in North America and throughout Mexico.
The species begins life by feeding on the roots of the youngest cucumber plants.
It then begins life as an adult that feeds on cucumbers and cucumber flowers.
The damage to cucumber plants is considerable when it comes to Spotted Cucumber Beetles.
Since these bugs impact the roots of young plants there are high chances these plants get to die even before they start producing cucumbers.
Other plants never reach their full potential despite surviving the bugs and their larvae.
The damage to the species expands to other plants as well.
You can find Spotted Cucumber Beetles on many types of host plants such as squash and beans. Even corn can suffer from these bugs.
Manually removing them and rotating crops are some of the oldest methods of reducing the impact of Spotted Cucumber Beetles.
16. American Rose Chafer
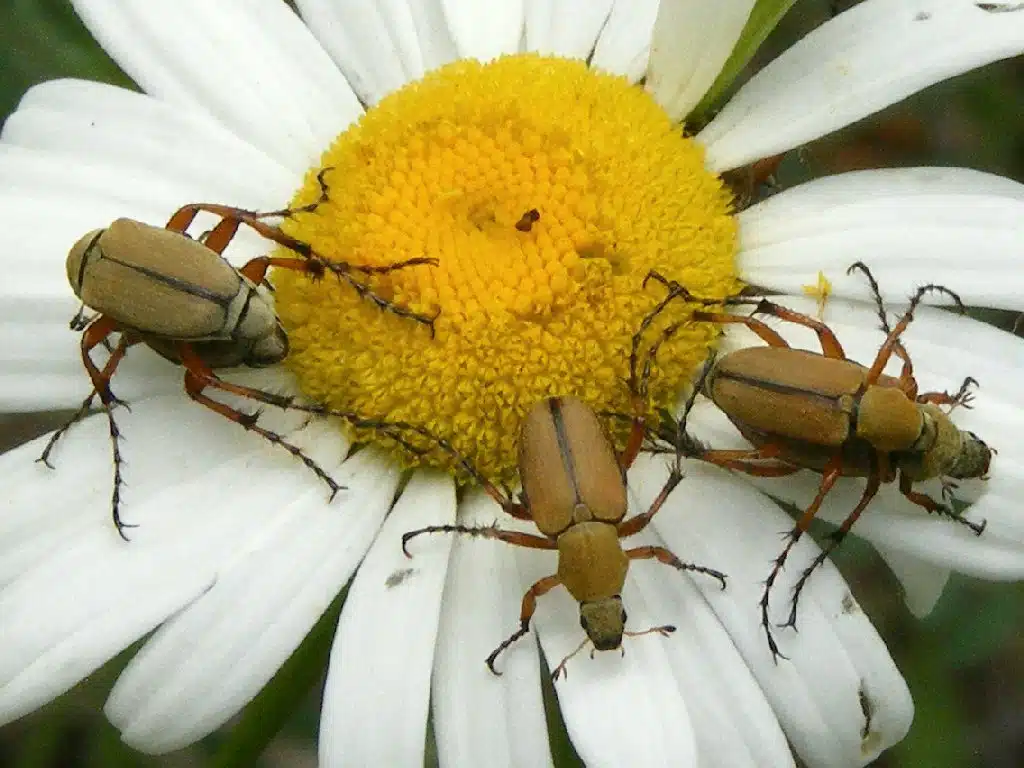

American Rose Chafers (Macrodactylus subspinosus) typically have a yellow-tan or yellow-light brown color. These bugs are known for their impact on gardens which is never negligible.
As their name implies, these bugs mostly feed on rose leaves and roses.
They also feed on grapes and apples among other plants and fruit trees.
The damages to roses tend to be considerable. This species is known for skeletonizing the leaves of roses.
They eat entire leaves to the point roses die.
One of the largest problems with American Rose Chafers is these bugs can often swarm. They can fly in their tens and hundreds.
Using receptors in the antennae, American Rose Chafers seek out roses and similar host plants in gardens.
They land on these host plants beginning to feed on leaves and stems.
American Rose Chafers have a mild impact such as reduced use in pollination in affected plants or a significant impact such as killing the plant altogether.
17. Yellow Velvet Beetle
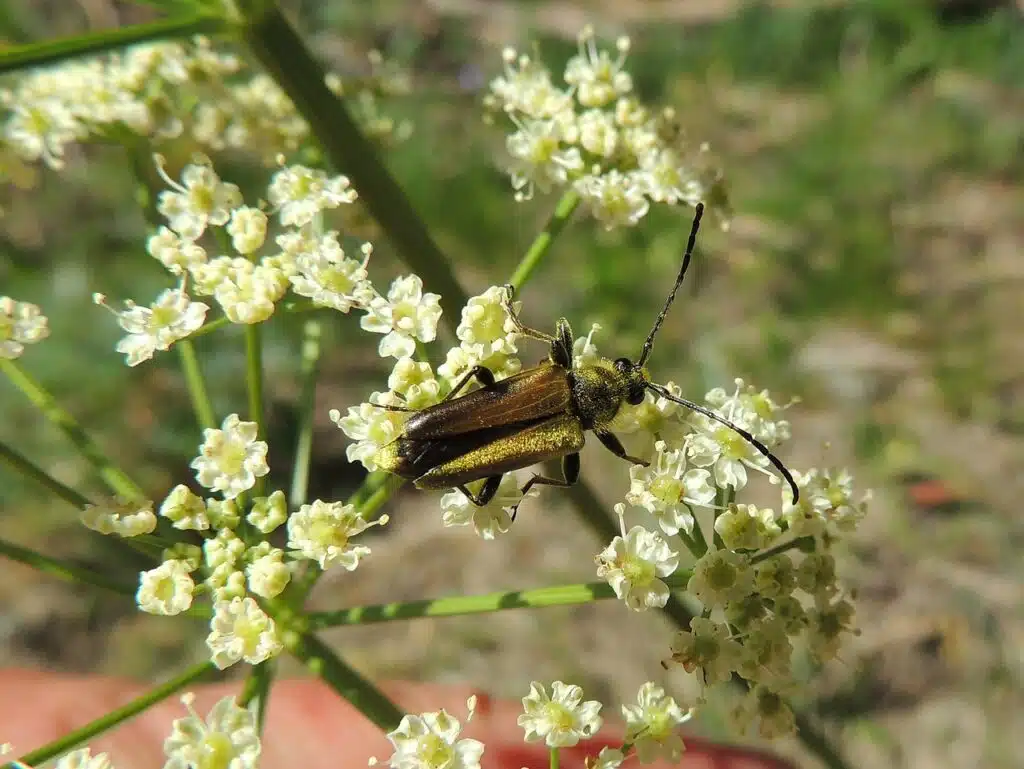

Yellow Velvet Beetles (Lepturobosca chrysocoma) grow to a maximum size of 2 inches. These yellow bugs are a common sight across the US and Canada.
The wings of the species have a golden-yellow color as does the head. The legs are black and covered in short yellow hair.
Yellow Velvet Beetles are among the species with the most significant impact on the tree canopy.
Feeding on leaves, impact apples and maples the most.
Early signs of an infestation include seeing a Yellow Velvet Beetle on the tree.
These bugs will eventually impact the health of the tree when its leaves will start to turn yellow.
This is also a point of no return for the trees themselves.
One of the ideal times to take action against the species is when you see holes in the tree bark. These are holes made for the larvae of the Yellow Velvet Beetle.
18. Yellow-striped Leafhopper
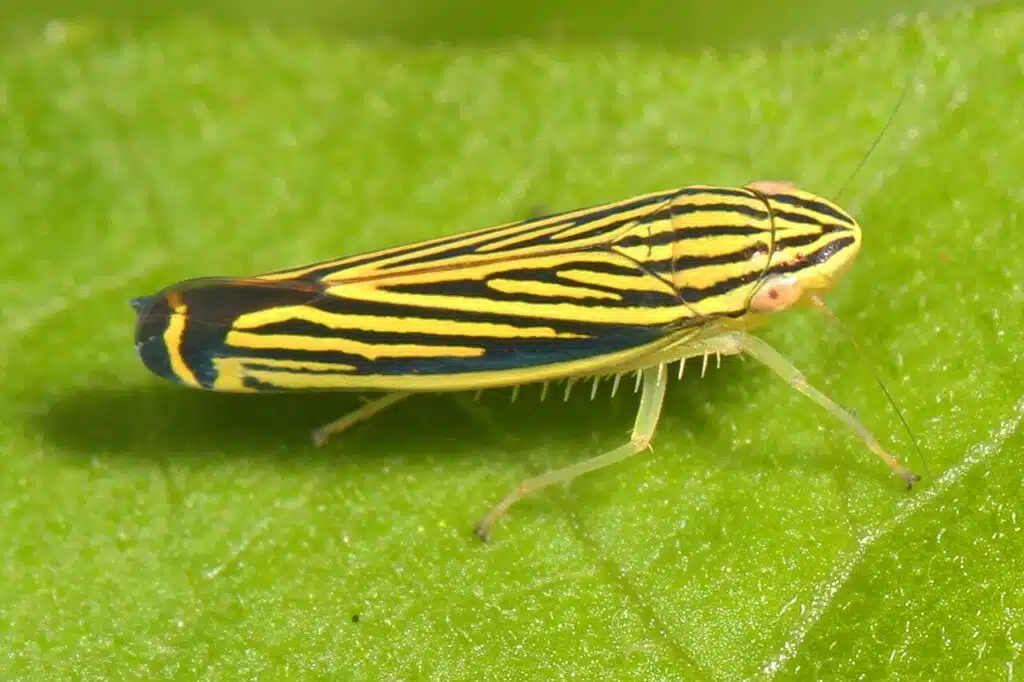

Part one of the largest insect species in the world, Yellow-striped Leafhoppers (Sibovia occatoria) have a considerable presence in Central and South America.
The species has multiple yellow stripes across its wings as well as yellow legs.
Bugs of this family are highly common in countries like Ecuador where they are seen feeding on the sap of various trees and plants.
Yellow-striped Leafhoppers have adapted legs that allow them to jump.
Bugs of this family are also known as pests on crops in certain countries.
They might even spread various bacteria which affect the leaves of their host species.
You can notice the impact of the species on decorative trees or other plants but the coloring of the leaves.
A clear sign of an infestation and possibly of bacteria spread by this yellow leafhopper include yellowing leaves.