Some bugs that bite are so small they can’t be seen without a magnifying glass or a microscope. Microscopic bugs can still bite. Some of them dig deep into the skin while others only bite on the surface level.
The results of these bites can be painful.
While the following bugs are microscopic, they can cause serious skin conditions such as eczema and rosacea.
Table of Contents
18 Microscopic Bugs That Bite
1. Scabies
Scabies is one of the most common microscopic bugs that bite.
These bugs are so small they can only be observed under the microscope.

Measuring around 0.5mm, scabies are some of the smallest bugs that bite.
Symptoms include rashes and red skin, which is the time people with scabies end up at a dermatologist.
These small bugs are white-brown and have 8 legs.
Careful examination of the infested skin shows scabies, the eggs of scabies, and their feces.
All of these cause itching and can even lead to infections.
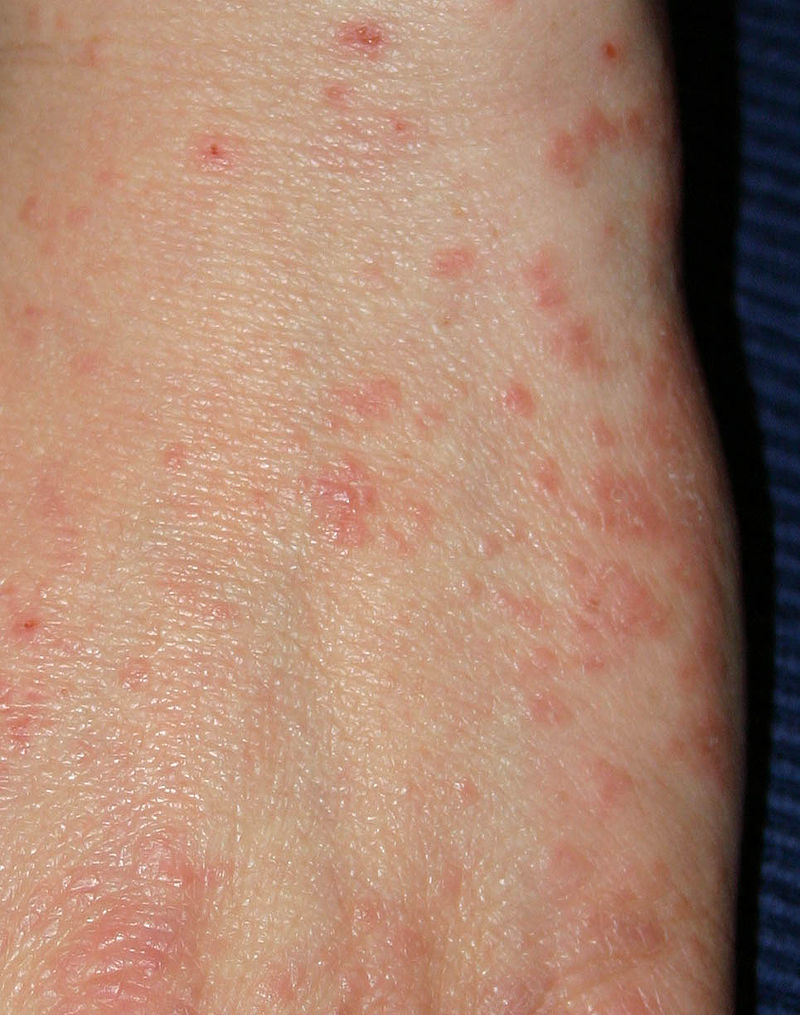
Scabies doesn’t begin to itch immediately after moving to a new person.
It can take up to a month for this species to multiply to the extent that skin starts to itch.
Scabies move by crawling as they cannot fly or jump. Prolonged contact with a person that has them is the only transmission method.
Public spaces such as hotels and hospitals are known for spreading scabies. Sexual contact with a person that has scabies also increases the chances of getting the bug.
Medication is needed to get rid of scabies which mostly settle on the hands.
Creams need to be applied to the affected area or often on the entire body. The right medical treatment depends on each individual according to the guidance of a doctor.
2. Chiggers
Chiggers are some of the smallest bugs that bite. They live in tall vegetation and are easily picked up in the summer.
Most chigger bites are seen on legs as they don’t have to travel up the body to bite.
Chiggers don’t bite the skin as they inject saliva into it.
This decomposes the skin to the extent that it makes it edible for bugs.
Extreme itching is very common in people who caught chiggers.

These small bugs aren’t visible without a good magnifying glass or a microscope.
Chiggers are known for changing their color after eating.
Most people only notice chiggers when facing itching skin or red marks of swollen skin.
Chiggers don’t burrow into the skin as scabies.
They live on the surface and they can be eliminated by following a medical treatment, typically with antihistamines.
Some actions can make their bites worse and even cause skin-level infections.
Hot showers and scratching are known for determining infections for people with chiggers.
3. Head and Body Lice
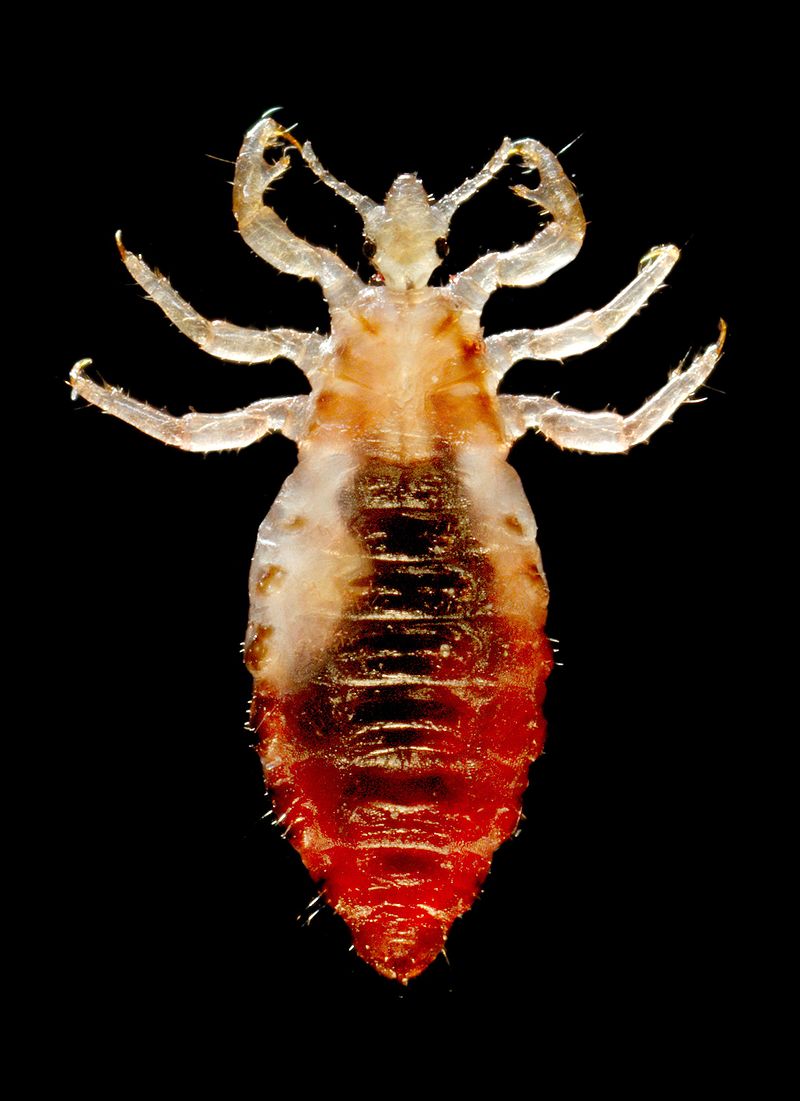

Head lice and body lice are common tiny bugs that bite and feed on human blood.
These small bugs are visible to the naked eye especially after they bite as they turn red or dark brown.
Head lice also lay eggs on the body. Most lice are white or slightly transparent and laid on the skin.
Head lice eggs or nits are laid on the base of the hairs. They are attached to hairs and they cannot be easily shaken off.
Lice are found in different areas of the body.
Various types of lice can live on humans. Head lice are found on the head while body lice are found on the rest of the body.
Lice are common in dirty places humans live in.
They are picked up in direct contact with a person that already has lice.
Homeless people and others that can’t shower or clean themselves quickly carry lice.
Dirty hotel rooms can also be a place that spreads lice.
Most people get lice in direct sexual contact with a person carrying these bugs or by sleeping in a place with lice.
Lice bites can be painful and cause itchy skin.
However, these small bugs can be eliminated without medical intervention.
A good cleaning session can eliminate lice from a person. Discarding all clothes and sheets that carry lice is important at this stage.
4. Pubic Lice
Pubic lice are a type of lice that only grows around the pubic area.
These lice are also visible, as are their eggs and bites.
Pubic lice spread through sexual contact and can be one of the types of lice that cause extreme itching.
Common symptoms of pubic lice attacks include extreme itching in the pubic area.
These small lice bite and they live skin marks.
These marks are typically red but they can turn blue in the case of repeated bites in the same area of the skin.
Pubic lice lay eggs in pubic hair. Eggs are identified by their white or yellow color.

Medical attention is sometimes needed in case of pubic lice cases.
People carrying these lice can also eliminate them on their own if there’s no infection.
Balms and shampoos that kill lice are ideally used to eliminate them.
These cosmetics are often applied to the whole body.
Shaving the body might be advisable at this stage as well.
Sharing clothes with a person that has pubic lice are known to spread these bugs.
People carrying pubic lice should refrain from touching or having sexual contact with others.
5. Straw Itch Mites
Straw itch mites are a common sight in areas with stored grains.
These mites aren’t visible and they normally infest dry grains in warehouses and other storage units.
Straw itch mites also bite people.
They inject saliva into the skin causing itchy skin.
These small bugs don’t cause severe adverse reactions with most bites. It’s only in extreme cases they can cause infections, nausea, and similar reactions.
Straw itch mites should be treated similarly to lice.
Washing clothes at high temperatures and maintaining good personal hygiene are recommended.
Straw itch mites are among the species you can kill with a good head lice shampoo.
Working in conditions where straw mites live requires wearing a uniform that is washed after every use.
6. Rat Mites
Rat mites mostly live on rats. They feed on the blood of rodents and enter homes with rats.
These small mites are only visible under a microscope.
They can migrate from rats to humans when a rat dies or when they cannot find any food or blood from rats.
Similar to lice, rat mites require proper attention to cleaning and washing up.
These small mites travel with rats and are common in all areas with rats such as old homes, dirty homes, restaurants, or hotels.
Rat mites migrate to humans looking for food.
They bite, turning red as they suck blood.
Rat mites further impact all other pets and animals around the house looking for a new source of blood.
Rat mites can also spread around the house in the case of a serious rat problem.
Cleaning and eliminating all foods that attract rats are needed to eliminate these microscopic bugs.
7. Bird Mites
Bird mites are known parasites that bite people.
As rat mites, bird mites primarily live on birds and poultry. They migrate from poultry to humans and they can bite looking for a blood meal.
Bird mites spread when in contact with birds that carry them.
Avoiding direct contact with poultry living in dirty conditions is recommended as the mites they carry move on to human skin.
Paying attention to dead birds and poultry is also recommended.
Bird mites start to migrate to a new host when their host dies.
These parasitic mites can move on to pets such as cats and dogs and then spread to the house and people.
Dealing with bird mite bites requires taking a good bath and using shampoos that kill lice.
Washing or discarding all clothes infested by bird mites is also mandatory.
People who suffer from bird mite bites might also need to apply skin-calming ointments.
8. Mange Mites
Mange mites are a type of small bug found on cats and dogs.
These mites bite pets for the blood. The human version of mites is scabies.
Mites come in various forms. Ear mites are found around the ears of pets and they can be transmitted to humans which they can also bite.
Canine scabies is another type of mange mites that is known to cause severe itching in dogs.
Canine scabies is a type of mange mites that can be transferred to humans. Some people might have severe allergic reactions to these mites.
All mange mites can then be transmitted to other animals around the house or around the farm.
Cows and horses can suffer from mange bites as well.
9. Flour Mites
Flour mites are common pantries with old flour on the shelves.
While flour mites do not bite, they cause all types of allergic reactions.
These small bugs are not visible to the naked eye as they can appear as dust when clumped together.
Flour mites can be identified as small white moving dust particles.
These mites can be eliminated only by updating the flour and dry grains in the pantry.
Discarding flour is one of the main actions to consider after identifying these small bugs which can be inhaled and cause respiratory issues.
10. Demodex Mites
Demodex mites are some of the beneficial small bugs that live on the face.
These mites are attached to the hair follicles on the face and they are known to be nocturnal.
Demodex mites come out at night and begin eating dead skin cells.
Mites of this genus lay eggs on the hair follicles of the face. They cannot be seen as the mites themselves.
Demodex mites do not have a painful bite and mostly go undiscovered.
They live up to 21 days.
Some people with skin reactions such as rosacea might visit a doctor for a clear diagnosis.
Doctors take skin samples that are examined under the microscope to look for Demodex mites.
These mites can sometimes cause other reactions such as red eyes.
Regardless of their reactions, they can be eliminated by frequently washing the face or by using a good cleanser regularly.
11. Green Lacewing Larvae
Green Lacewings are some of the most beneficial insects in parks in gardens.
They feed on all types of invasive insects and they help control their numbers and the damages they cause.
Adults don’t bite but their larvae have been known to bite.
Green Lacewing Larvae have an elongated body of a brown-yellow color.
These larvae can bite people handling plants and foliage they grow on.
The bite isn’t severe or painful. A small pinch is the best description for the otherwise rare bite of the Green Lacewing larvae, mostly when working in the garden.
12. Thrips

Thrips are known for having sharp mouthparts they use to pierce plants to suck sap.
Both thrips and their larvae have been shown to bite people.
A good number of their bites occur while camping, trekking, or when relaxing out in nature in parks or gardens.
The bites of thrips aren’t painful. They lead to small blotches of red skin, at best.
Thrips are winged insects which means they can make it on different parts of the bite and bite accordingly.
As with mosquitoes, thrips hate the smell of insect repellents. Applying insects and mosquito repellent on the skin can keep thrips away.
13. Tiny Ants
Tiny ants can sometimes bite. Not all ants that are small bite but there are at least a few hundred that can bite humans.
Tiny ants such as Acrobat ants are known to bite.
Small and black, these ants have minimum effect on the bitten area. Mild discomfort and red skin are common reactions to the bite of the species.
Tiny ants such as Acrobat ants are most dangerous when they live in areas infested by aphids or scale insects.
These types of invasive species release a honeydew substance on plants. The sweet substance attracts these ants that eat sugary foods.
Dealing with such plants by hand can often leave you exposed to Acrobat ants and their bites.
Most bites of these small ants are harmless. Their reactions are minimal.
Applying ice to the bitten skin area is one of the recommended tactics to reduce the itching or swollen skin.
14. Fleas

Fleas are small bugs that live on animals and which also bite humans.
They feed on human blood and they insert saliva into the skin which causes reactions such as extreme itching.
Fleas are easily picked up from an infected pet or from another person that has fleas.
The bites are identified by a discolored ring around the bitten area.
Multiple treatments are available for the bite of these small bugs.
While they appear as small black dots on the skin, fleas can have a painful bite that requires attention.
Antihistamines are often recommended for flea bite symptoms.
Plants that reduce inflammation such as chamomile are also recommended on the skin in the bitten area.
You can prevent fleas on your pets by washing them with anti-flea shampoo.
Further Reading:
15. Bed Bugs
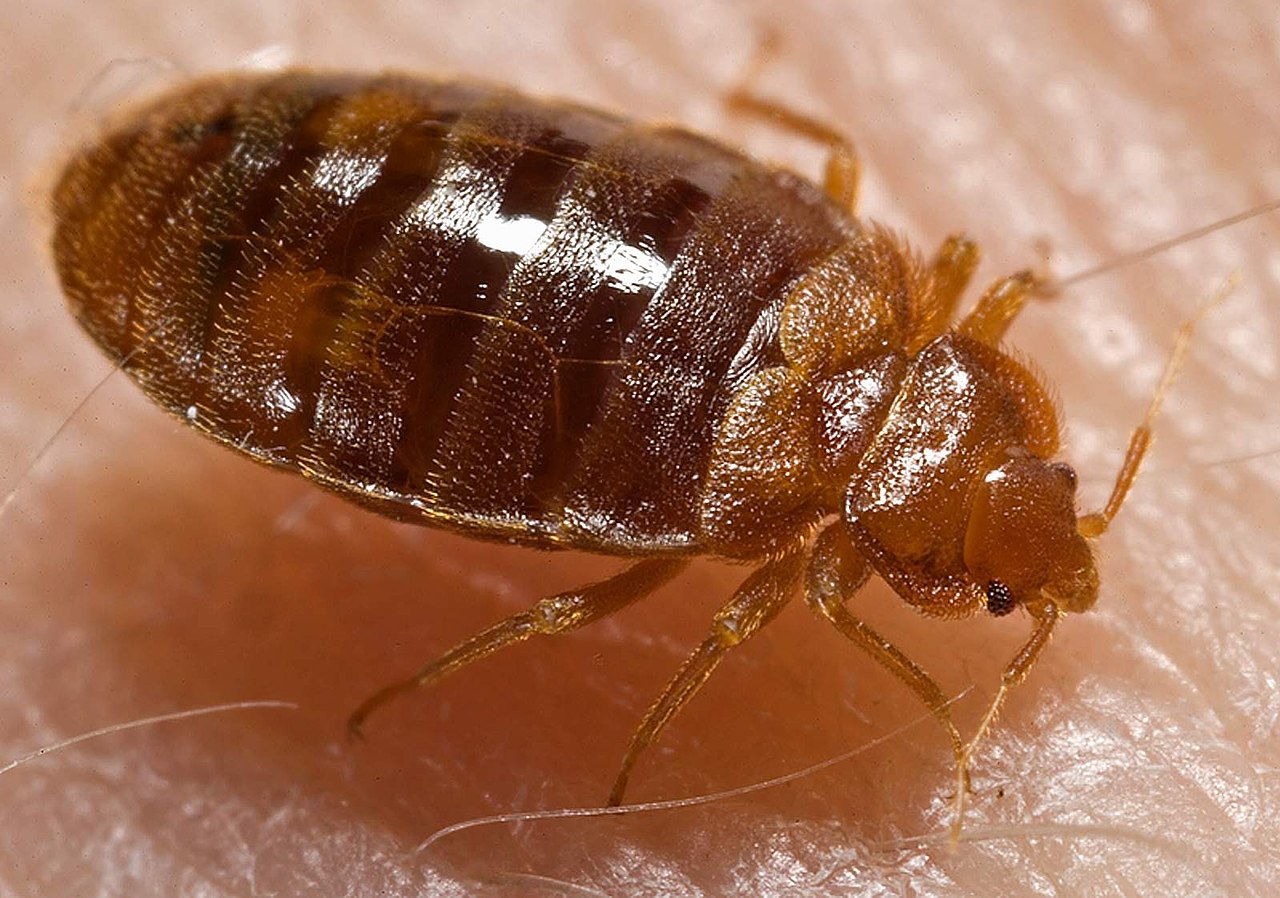

Bed bugs are known to have tiny dark oval-shaped bodies.
These bugs often live on the bed where they easily transition to the skin. These bugs bite as they need blood to survive.
Bites of these bugs are identified according to exposed areas of the skin.
If other bugs such as fleas bite your ankles, bed bugs can bite any area of your body that’s exposed.
Attracted to breath and warmth, bed bugs can bite repeatedly at night leading to itchy skin and red marks all over the body in the morning.
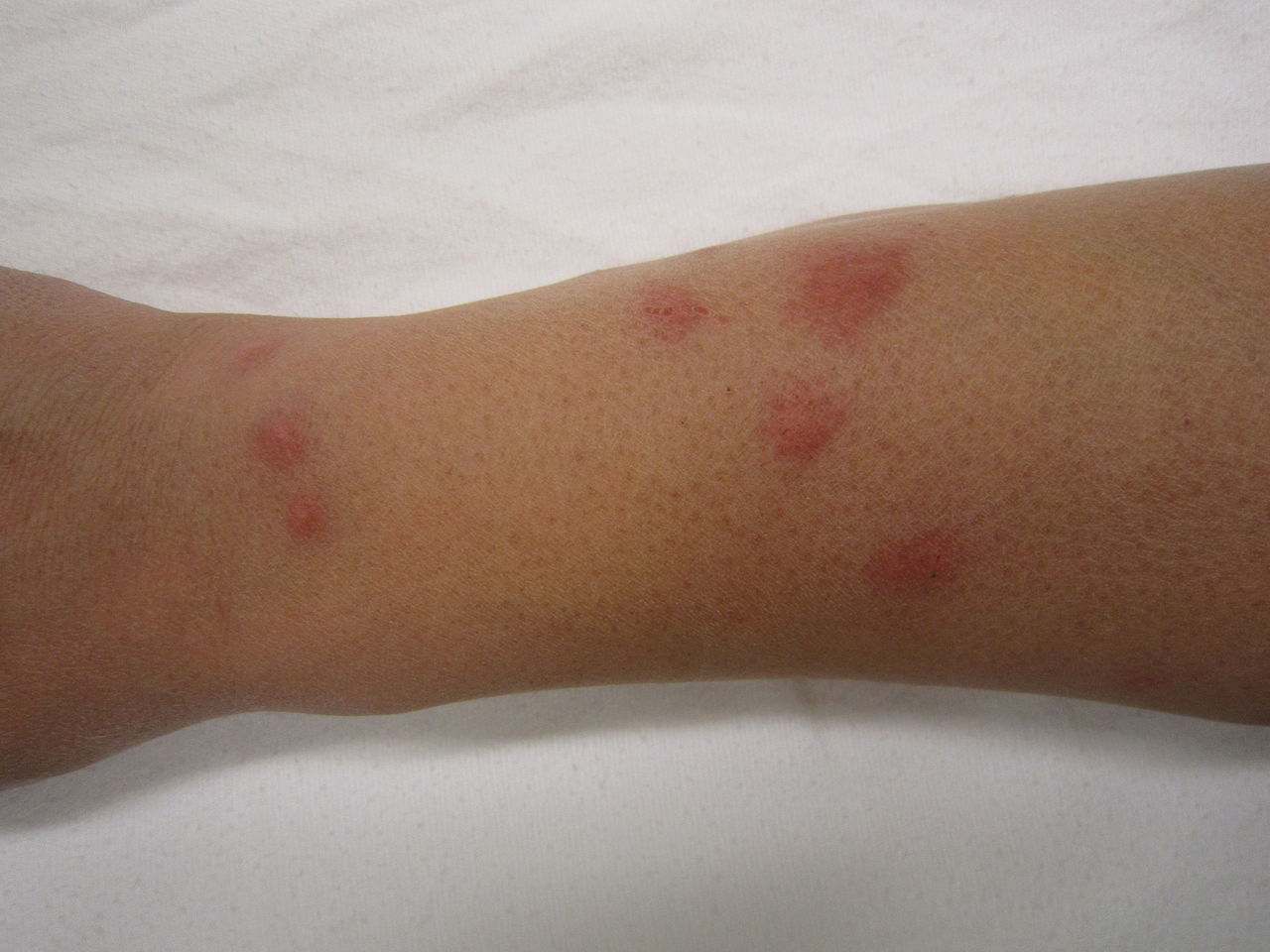
Eliminating the risk of bed bugs requires following regular cleaning routines.
You need to vacuum the area of the bed and the house frequently.
Eliminating all types of clutter around the bed and the house is also advisable to clear out all possible hiding places for bed bugs.
Further Reading:
16. Mosquitoes
Mosquito bites are common in areas with sitting water where these insects lay eggs.
Mosquitoes like humid environments and infested water which means they carry diseases such as malaria or the West Nile virus.
Mosquito bites can lead to itchy skin, severe allergic reactions, and mosquito-borne diseases.
They can be prevented by wearing long-sleeve clothes and clothes that cover as much skin as possible.
Keeping mosquitoes out of the house is possible by planting repellent plants or by spraying essential oil.
Mosquito bites that itch can be dealt with by applying over-the-counter ointments.
Applying ice cubes to the bites helps reduce itchiness as well.
A doctor’s visit is only required for severe reactions.
This can include a skin-level infection caused by scratching or even by showing signs of an early fever.
17. Black Flies

Black flies can bite people. These types of flies are common all around the world.
Buffalo gnats are an example of a tiny black fly that bites people.
Females of the genus bite humans for the blood. They need a lot of blood to reproduce or to lay more eggs.
These types of flies are so small they can sometimes be overlooked.
Eliminating all foods flies are attracted to from the house is recommended to stay away from the bites of these flies.
Medical attention isn’t recommended when the bites aren’t followed by more severe reactions.
Washing the skin with soap and water is recommended following a bite from these small flies.
Scratching is as bad as another type of bug bite and is to be avoided to keep skin infections away.
18. No-see-ums

No-see-ums are very small flying insects that can bite similarly to mosquitoes.
They come out in the summer from areas with high moisture and they are known for their impact when it comes to painful bites.
No-see-ums have some of the most painful bites for bugs that are only 1-3mm large.
Eliminating puddling water and clearing the drains around the house are among the common measures taken to reduce the risk of no-see-um bites in the summer.
The bites of these insects don’t require hospitalization. They need to be washed with soap and water.
Some no-see-um bites lead to swollen skin while others don’t.
You can apply ice cubs on your bites if no-see-ums have led to swollen red skin marks.
Calming balms can also be applied to the bitten area to calm the itchy skin.
What Else It Could Be? (If not a bug)
Not all itches and red spots on the skin are caused by bug bites. Certain skin conditions can feel just as itchy.
Your skin can also suffer when reacting to certain fabrics or some type of medication.
Some types of skin condition
Various types of skin conditions can be confused with bites from microscopic-size bugs.
You might be suffering from any of the following conditions which may or may not come with itchy skin, red skin, discolored skin, or irritation.
- Diabetes
- Eczema
- Acne
- Rosacea
- Fungal infections
- Hypothyroidism
- Hives
A reaction to fabrics and materials
Dry skin in contact with certain materials can trigger allergic reactions or even itchiness. Dry skin is common in the winter.
Certain materials such as natural wool, fiberglass, strong cleaning chemicals, or insecticides can cause skin reactions.
Direct contact with these materials can sometimes lead to red skin, itchy skin, or even swollen skin.
A side effect of medication or drugs
Medication and drugs are among the most common causes of some types of biting sensations. Steroids, cocaine, heroin, and other types of recreational drugs may also cause these biting sensations.
Side effects to all types of chemicals and medication are among the reasons to visit a doctor.
What Should You Do When You Are Bitten
Bites of microscopic bugs can sometimes be identified correspondingly without a doctor.
Lice can be seen on the body without visiting the doctor.
Other microscopic bugs might not be visible on the skin. Scabies might need a doctor’s appointment for correct identification.
Here’s what to do if you are bitten by a microscopic bug or if you think you’ve been bitten by one of these bugs.
Apply ice (on swollen or itchy skin)
One of the first things to do when you suffer from these bites is to apply ice.
A simple ice cube can reduce itchiness and puffiness.
Ice is a quick remedy that might not work for more than a few hours. Re-applying ice multiple times per day on the bitten area might be required until you get to a doctor.
Washing the skin with soap and water is recommended before applying ice. This eliminates the risk of rubbing in bug feces which can lead to further inflammation.
Ice cubs need to be applied on the skin for up to a few minutes to have a sensible effect.
Refrain from scratching
Scratching is a constant urge when dealing with bugs such as head lice or scabies. Scratching comes with plenty of risks, however.
The biggest risk of scratching is starting a skin infection.
This is possible when you rub in bug feces, dirt, or dead skin cells in the bitten area.
Scratching is not recommended with any type of bite, especially with bug bites.
Bugs that bite come from animals, dirty places, or dirty people without the capacity to clean themselves.
This means they carry all types of bacteria that can cause infections.
As an example, scabies carries the following bacteria.
This bacteria has been shown to cause secondary skin problems following bites such as skin infections.
Treating infections delays the treatment of the bug bite in general. Doctors have to treat infections first.
Talk to a doctor
A general practitioner or a dermatologist can advise on the best treatment options for microscopic bug bites.
This treatment can last weeks and it’s best to plan it with a doctor.
Some type of treatment only involves cleaning and applying creams while other treatments require taking medication.
Here’s how to help the doctor establish the correct treatment.
Take a bug sample to the doctor if possible.
Don’t start using medication on your own
Doctors can take skin samples to determine the exact type of bug causing skin problems and health issues.
These samples are analyzed and treatment is only recommended after correct bug species identification.
Don’t begin treatment on your own
Treating your skin condition with medication or other types of ointments might not be a good idea.
Some bugs such as lice can be treated at home with special shampoos you get at pharmacies.
Other bug bites require medical attention.
Starting treatment on your own isn’t advisable with the more severe bites.
Taking drugs without medical permission is not recommended.
Antihistamines are used against bug bites often.
These drugs are used in cases with allergies such as skin allergies, eye irritation, and other reactions to bug bites and insect bites of an allergic nature.
You should take antihistamines after talking to a pharmacist or a doctor.
Refrain from spraying pesticides in your home
Pesticides kill many types of microscopic bugs such as lice and bed bugs.
These potent chemicals are used by professional pest controllers but using them on your own can be dangerous.
Pesticides can trigger further skin allergies essentially worsening your condition.
Some of the typical reactions to pesticides include the following.
- Irritated skin
- A runny nose
- Itchy eyes
- Respiratory problems
- Headaches
- Dizziness
In extreme cases, prolonged exposure to pesticides can even kill people.
As a result, it’s best to refrain from applying pesticides yourself to eliminate the microscopic bugs.
Don’t use home remedies on the skin
Home remedies can sometimes work on the skin. Without knowing which type of bug is causing the issues you might be inflicting more harm.
Here are a few common home remedies you should stay away from until you can correctly identify the bug causing the skin issues.
- Creams
- Ointments
- Bandages
- Topical tea application
- Face scrubs
A doctor can prescribe the right treatment according to the type of bug that’s biting you.
If your bites are caused by head lice or pubic lice you can get various shampoos and soothing creams from a pharmacy.
These aren’t typical shampoos as they are especially formulated against lice.
Don’t get in close contact with other people
One of the mistakes people often make is asking friends or family members to inspect potential skin conditions following the bites of these small bugs.
While a second opinion can help, it’s best to refrain from close physical contact with other people.
Both scabies and lice, some of the most common microscopic bugs spread through physical contact.
These bugs cannot fly or jump and they are limited to transferring hosts when they meet each other for a prolonged time.
Sexual contact is to be especially avoided when suffering from these skin conditions such as rosacea and irritation.
This type of physical contact is to be avoided for weeks when treating lice, as the treatment can take up to a few weeks.
Here’s how long it takes to treat some of the most common bites these microscopic bites.
Scabies – 1-2 weeks
Pubic lice – 1-2 weeks
Head lice – 1-3 weeks
Chiggers – 1-3 weeks
Demodex mites – 1-3 weeks
Bed bugs – 3-6 weeks
How to Prevent Microscopic Bug Bite
Preventing the bites of these bugs is the best option when it comes to maintaining healthy skin.
Here are a few recommendations when it comes to keeping these bugs that bite away.
Avoid physical contact with people carrying tiny bugs that can bite
Physical contact is to be avoided when it comes to keeping biting microscopic bugs away.
Short contact such as shaking hands isn’t considered high risk.
Prolonged sexual contact is of high risk.
Sleeping in a bed with bed bugs is guaranteed to transmit these biting bugs to a new person.
Petting a dog that carries these bugs for a few minutes is also known to transmit various biting bugs.
Check your pets for these bugs regularly
One of the preventive measures you can take is to check children and pets for microscopic bugs such as lice.
A flashlight and a magnifying glass can always help in finding these bugs or signs of the bugs such as eggs and feces.
Regular checks are recommended for pets that spend a lot of time in parks and gardens or who spend a lot of time with other pets.
The same tactic is recommended for children of kindergarten or school age.
Wear long sleeve clothes when out in nature
Another good preventive measure is to wear clothes that cover as much skin as possible when camping or when spending time out in nature.
A walk in the woods can come with its risks such as picking up ticks or thrips.
Long pants and tops with long sleeves are always recommended when it comes to lowering the risk of being bitten by all types of tiny biting bugs.
Trim vegetation around the house
Some biting bugs such as mosquitoes thrive in damp conditions. These conditions can be favored by the tall vegetation around the house.
Both mosquitoes and other bugs easily thrive around homes with tall grass, shrubs, and tall unkept flowers where water doesn’t evaporate quickly.
Shaded places are cool damp areas where many of these bugs reproduce.
Maintain good body hygiene
A simple routine task such as taking a daily shower can keep microscopic bugs away.
Poor personal hygiene is one of the main reasons bugs such as lice exist.
In the US, lice are mainly reported in homeless people that can’t bathe or clean themselves.
Lice are also found in areas where homeless people live.
Good personal hygiene is also important when it comes to washing the hair which can be a breeding ground for lice and their eggs.
Cleaning the nails, washing the beard, and taking a shower after a long walk in nature are all small steps that can keep many microscopic bugs away.
Fleas are known to develop in the areas of the house or of the yard where pets rest.
This means even pets and animals need to have a regular cleaning routine.
Fleas are often carried indoors by cats and dogs and it’s best to check these pets as well.
Wildlife can also help spread fleas so you need to ensure your pets don’t get in contact with wild animals apart from washing them regularly.
Summary
Microscopic bugs can bite and they can do so without you noticing immediately.
Most of these bugs cause serious skin conditions which may only be visible a few days or a few weeks after they have settled on a new person or host.
Most biting bugs are dangerous as they cause itching and can cause infections.
They can also transmit diseases and spread to others. Some of these conditions require medical attention. Treating the bites of microscopic bites can require a treatment that lasts up to a few weeks.